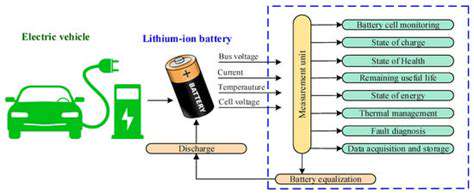
Comparing Battery Management Systems in Modern EVs
Centralized Battery Management System (BMS)
When examining battery management systems, the centralized BMS architecture stands out for its straightforward design. This system relies on one primary processing unit to oversee all battery operations, from monitoring individual cells to managing charging cycles. While this simplicity offers advantages for smaller installations, it does create a vulnerability - if the central unit fails, the entire system may be compromised. For budget-conscious projects where occasional downtime isn't catastrophic, this architecture provides an economical solution.
The data handling capabilities of centralized systems deserve special attention. With all information flowing to a single point, technicians can quickly assess overall battery health and identify patterns that might indicate future issues. This consolidated approach to diagnostics often leads to faster problem resolution and more accurate maintenance predictions. The ability to generate comprehensive reports from a unified data source proves particularly valuable for operations requiring detailed performance documentation.
Decentralized Battery Management System (BMS)
Distributed systems take a fundamentally different approach by equipping each battery module with its own monitoring and control capabilities. This design philosophy significantly improves system resilience - if one module encounters problems, the others can continue operating normally. The automotive industry frequently adopts this architecture for electric vehicles, where reliability is paramount and system failures could have serious consequences.
Response time represents another key advantage of decentralized systems. Localized control units can detect and respond to abnormalities within milliseconds, often preventing minor issues from escalating into major failures. This rapid response capability makes decentralized architectures ideal for applications where safety is critical or where batteries operate in challenging environmental conditions.
Hybrid Battery Management System (BMS)
Many modern installations now implement hybrid solutions that blend the best features of both architectures. These systems maintain local control at the module level while incorporating centralized oversight for comprehensive system management. This balanced approach provides redundancy against failures while still enabling coordinated system-wide optimization.
The flexibility of hybrid systems makes them particularly suitable for large-scale energy storage applications. They can scale efficiently as battery banks expand, maintaining both detailed local control and broad system visibility. This adaptability explains why hybrid architectures are becoming increasingly popular in grid storage and industrial applications where both reliability and data integration are crucial.
Key Performance Metrics: Comparing BMS Effectiveness
Revenue Growth
Revenue analysis serves as the foundation for evaluating any business's trajectory. Tracking income expansion reveals how effectively an organization converts opportunities into financial results. When comparing growth rates against industry standards and historical performance, management gains actionable insights into strategy effectiveness. The most successful companies don't just monitor revenue totals - they analyze the specific drivers behind increases, whether from new product adoption, market expansion, or improved customer retention.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Calculating the true expense of gaining new customers requires examining all related expenditures - advertising campaigns, sales team compensation, promotional materials, and associated overhead. Organizations that maintain optimal CAC levels typically demonstrate efficient marketing operations and strong product-market fit. When this metric rises disproportionately to customer value, it often signals the need for strategic adjustments in targeting or messaging.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Forward-thinking businesses recognize that initial sales represent just the beginning of customer relationships. CLTV analysis projects the total revenue stream from each client, considering repeat purchases, upsell opportunities, and referral potential. Companies that excel at nurturing long-term customer relationships often see CLTV figures that far outweigh acquisition costs. This metric becomes particularly insightful when segmented by customer type or acquisition channel.
Conversion Rate
The percentage of prospects who complete desired actions serves as a direct measure of marketing effectiveness. High conversion rates typically indicate strong alignment between customer needs and business offerings. Savvy marketers track conversion metrics at each stage of the customer journey, identifying specific points where potential buyers disengage. This detailed analysis enables precise optimization of websites, sales processes, and marketing communications.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Customer loyalty metrics provide invaluable insights into brand health. The NPS system categorizes customers based on their likelihood to recommend products or services, creating a clear indicator of satisfaction levels. Businesses with consistently high scores typically enjoy organic growth through word-of-mouth referrals. Regular NPS tracking helps organizations identify service improvements that can transform satisfied customers into passionate advocates.
Website Traffic and Engagement
Digital analytics offer a window into how potential customers interact with online properties. Beyond simple visitor counts, engagement metrics reveal how effectively content captures attention and guides users toward conversion. Pages that maintain visitor interest while naturally leading to desired actions typically demonstrate optimal design and messaging. These insights prove particularly valuable when testing new content strategies or site layouts.
Brand Awareness and Sentiment
Measuring brand recognition and perception helps organizations understand their market position. Tracking studies can reveal whether marketing investments are effectively building mindshare, while sentiment analysis uncovers emotional connections with the brand. Companies that regularly monitor these metrics can adjust positioning strategies before minor issues become significant problems. In crowded markets, strong brand differentiation often makes the difference between success and obscurity.
Selecting the ideal location represents perhaps the most impactful decision in retreat planning. The environment should perfectly complement the experience participants seek. Whether envisioning a secluded mountain sanctuary for deep reflection, a vibrant coastal setting with ocean views, or a tranquil countryside escape, each option creates distinct possibilities. Thorough research into potential venues should include reviewing participant testimonials, assessing available amenities, and evaluating the overall ambiance of retreat centers.
Advanced Features and Technologies in Modern BMS
Advanced Battery Monitoring Capabilities
Contemporary battery management solutions have evolved far beyond basic charge monitoring. Modern systems employ sophisticated algorithms that track multiple performance parameters simultaneously, including thermal characteristics and internal resistance changes. This comprehensive monitoring enables early detection of potential issues, allowing for preventive measures that can dramatically extend battery service life. The most advanced systems can pinpoint developing problems to specific cells, enabling targeted maintenance that minimizes downtime.
Predictive Maintenance and Proactive Management
The integration of predictive analytics represents a major leap forward in battery management. By analyzing performance trends and comparing them against known failure patterns, these systems can forecast potential issues before they occur. This shift from reactive to proactive maintenance significantly reduces unexpected failures while optimizing maintenance schedules. Advanced systems can even adjust operating parameters in real-time to compensate for aging components, maintaining optimal performance throughout the battery's lifecycle.
Intelligent Thermal Management
Temperature regulation has become increasingly sophisticated in modern BMS designs. Advanced modeling techniques allow systems to anticipate thermal changes based on usage patterns and environmental conditions. This predictive capability enables preemptive adjustments to cooling systems, preventing temperature extremes that could degrade battery performance or safety. The most effective thermal management strategies maintain cells within their ideal operating range while minimizing energy consumption for cooling.
Enhanced Safety Mechanisms and Protection
Safety systems in contemporary BMS designs address a comprehensive range of potential failure modes. Beyond basic voltage monitoring, these systems can detect subtle changes in cell behavior that may indicate developing problems. Multi-layer protection architectures ensure backup safety measures remain available even if primary systems experience issues. This comprehensive approach to safety is particularly critical in applications where battery failures could have severe consequences.
Integration and Communication Protocols
The ability to seamlessly integrate with broader system architectures has become a hallmark of modern BMS solutions. Standardized communication protocols facilitate data exchange with vehicle control systems, charging infrastructure, and maintenance platforms. This interoperability enables comprehensive system optimization while simplifying diagnostic processes. As vehicle architectures become more complex, robust communication capabilities will continue growing in importance.
Future Trends and Challenges in BMS Development
Emerging Technologies Shaping BMS Design
Battery management technology continues evolving rapidly, with several innovations poised to transform system capabilities. Next-generation sensors promise even more precise monitoring of battery health indicators, while improved data processing techniques will enable more sophisticated analysis. Wireless communication technologies are reducing system complexity while improving data accessibility. These advancements will support increasingly intelligent battery management strategies that adapt to both immediate conditions and long-term usage patterns.
Enhanced Safety Features for Improved Reliability
Future safety systems will likely incorporate more advanced failure prediction capabilities, potentially using machine learning to identify subtle precursors to catastrophic events. Thermal management will become more precise, with the ability to regulate temperature at the individual cell level. These improvements will be particularly valuable as battery energy densities increase, creating greater safety management challenges. Redundant safety architectures will become standard in critical applications, ensuring backup protection remains available under all conditions.
Data Analytics and AI Integration for Predictive Maintenance
The application of artificial intelligence in battery management is opening new possibilities for predictive analytics. By processing vast amounts of operational data, these systems can identify complex patterns that human analysts might miss. This capability enables more accurate remaining life predictions and more precise maintenance scheduling. As these technologies mature, we can expect battery management systems that continuously learn and adapt to specific usage patterns, optimizing performance for each unique application.
Addressing Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
While advanced features offer significant benefits, cost remains a critical consideration for widespread adoption. Future developments will likely focus on achieving greater functionality without proportional cost increases. Modular designs that can scale from small to large applications will help address diverse market needs. The most successful future BMS solutions will balance advanced capabilities with practical affordability.
Addressing the Challenges of Varying Battery Chemistries
The proliferation of battery technologies presents both opportunities and challenges for BMS developers. Future systems will need to accommodate an expanding range of chemistries, each with unique characteristics and requirements. Flexible architectures that can be adapted through software configuration rather than hardware changes will provide significant advantages. This adaptability will be crucial as battery technology continues evolving rapidly, with new formulations regularly entering the market.
Read more about Comparing Battery Management Systems in Modern EVs
Hot Recommendations
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies
- The Global Push for Long Duration Energy Storage
- Renewable Energy and Job Creation: A Growing Sector
- Energy Storage in Commercial and Industrial Applications
- Direct Air Capture (DAC) Powered by Renewable Energy