How Plug in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) Reduce Emissions
Table of contents
- PHEVs combine electric propulsion with combustion engines, reducing emissions significantly.
- Charging behavior and infrastructure affect PHEV emission reduction potential.
- Government incentives encourage PHEV adoption by lowering costs.
- PHEVs can lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional vehicles.
- Technological advancements enhance PHEV performance and efficiency.
- PHEVs improve urban air quality by reducing pollutants.
- Smart charging can amplify renewable energy use and minimize waste.
- Education on PHEV benefits can enhance consumer acceptance.
The integration of PHEVs supports sustainability and energy independence goals.
Understanding Emission Reduction Through Electric Power
Overview of Electric Power in Transportation
Electric power plays a crucial role in the transportation sector, particularly with the rise of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). These vehicles combine traditional internal combustion engines with electric propulsion, allowing for a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, PHEVs can reduce emissions by up to 40% compared to conventional gasoline vehicles, depending on driving habits and charging practices.
The shift towards electric power is more than just a technological change; it represents a paradigm shift in how we think about mobility and energy use. As the grid becomes greener, fueled by renewable energy sources, the emissions reductions achieved through PHEVs are expected to improve further. The integration of electric power into transportation not only targets air quality improvements but also contributes to energy independence and sustainability efforts.
Impact of PHEVs on Emission Reduction
The potential of PHEVs to cut emissions has been embraced by consumers and manufacturers alike. Research from the International Council on Clean Transportation indicates that PHEVs typically emit 60% fewer pollution particles compared to conventional vehicles. This substantial reduction can play a vital role in urban areas where air quality is a pressing concern.
Charging Infrastructure and User Behavior
The effectiveness of PHEVs in reducing emissions heavily relies on charging infrastructure and user behavior. For instance, frequent charging at home or public stations can maximize the use of electric power, minimizing reliance on fossil fuels. Studies show that drivers who strategically plan their charging can significantly extend their electric-only range, resulting in lower operational emissions. Thus, enhancing charging infrastructure is crucial, as it facilitates a smoother transition to electric power.
Moreover, user behavior plays a pivotal role. Those who are aware of their vehicle's electric capabilities and actively engage in efficient driving habits tend to experience greater benefits in terms of emissions reduction. Offering educational resources on charging optimally can further enhance the environmental benefits of PHEVs.
Future Prospects for Emission Reduction through Electric Power
Looking ahead, the Future of PHEVs seems promising in the context of global emission reduction efforts. With advancements in battery technology, such as increased energy density and faster charging capabilities, the appeal of PHEVs is expected to grow. Additionally, government incentives and regulatory frameworks aimed at encouraging cleaner transportation alternatives will likely result in broader adoption of PHEVs and electric vehicles overall.
It’s essential to continue monitoring and supporting these developments, as the full sustainability potential of PHEVs hinges on continuous improvements in both vehicles and charging infrastructure. Engaging various stakeholders—governments, manufacturers, and consumers—will be key in creating a holistic approach to emission reductions in the transportation sector.
Enhanced Fuel Efficiency Compared to Traditional Vehicles
Understanding PHEVs and Their Efficiency Benefits
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) combine traditional combustion engines with electric propulsion systems, providing a unique balance of performance and sustainability. This dual approach allows PHEVs to significantly enhance fuel efficiency, offering drivers the ability to operate primarily on electric power for shorter trips while still having the internal combustion engine at their disposal for longer journeys. The integration of both technologies results in less reliance on gasoline, thereby reducing overall fuel consumption.
Research indicates that PHEVs can achieve up to 80 miles per gallon equivalent (MPGe) in city driving situations, outperforming standard gasoline-powered vehicles. This efficiency is primarily due to the vehicle’s capacity to operate on electric power alone for daily commuting needs, cutting fuel costs and emissions substantially. With increasing advancements in battery technology, the electric-only range of PHEVs continues to improve, further boosting their appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Cost Savings and Financial Incentives
In addition to environmental benefits, the economic advantages of owning a PHEV are noteworthy. Many drivers experience substantial savings on fuel costs, especially in urban environments where shorter trips are more common. A report from the U.S. Department of Energy suggests that the average annual savings from operating a PHEV can be upwards of $1,500 compared to traditional vehicles. This figure emphasizes the financial appeal of investing in cleaner transportation options.
Government Programs and Support
To encourage the adoption of PHEVs, various governments offer financial incentives, including tax credits and rebates. In the United States, federal tax credits can reach up to $7,500 for qualifying PHEV models, while many states provide additional benefits. These incentives not only lower the initial purchase price but also promote a shift towards more sustainable transportation choices among consumers.
Beyond financial incentives, some regions have also initiated programs that facilitate access to charging infrastructure, ensuring that PHEV owners have convenient options for recharging their vehicles. Local governments are investing in public charging stations, further enhancing the usability of PHEVs and making the transition to cleaner vehicles more viable for a larger audience.
Impact on Emissions Reduction
One of the most significant advantages of PHEVs is their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, PHEVs emit fewer pollutants compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, particularly when operating in electric mode. This transition towards electric driving not only decreases tailpipe emissions but also contributes to cleaner air quality in urban areas.
Moreover, the energy used to charge PHEVs increasingly comes from renewable sources such as wind and solar, amplifying their environmental benefits. As the grid becomes greener, the lifecycle emissions of operating PHEVs are expected to decline even further. It is crucial for consumers to consider both the emissions produced during driving as well as the source of electricity when evaluating the overall environmental impact of their vehicles.
Contribution to Renewable Energy Integration
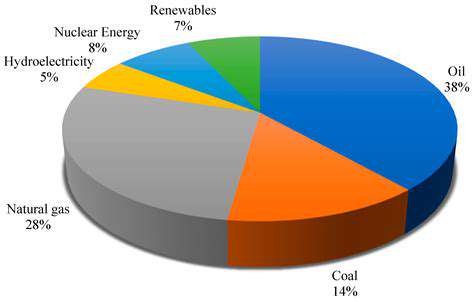
Impact on Grid Stability and Demand Response
Integrating Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) into the energy grid plays a vital role in enhancing grid stability. By allowing PHEVs to be charged during off-peak hours, Demand for electricity can be managed more efficiently. This practice not only helps to balance supply and demand but also reduces the reliance on fossil fuels during peak periods.
Studies indicate that if just 10% of vehicles on the road were PHEVs, they could provide substantial backup capacity to the grid, equivalent to 2-3 gigawatts of energy. This capability can significantly ease the pressure on utilities as they strive to integrate more renewable sources into their energy mix. Furthermore, utilities can benefit from utilizing vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, enabling PHEVs to discharge energy back into the grid during high-demand situations.
Enhancing Renewable Energy Utilization
PHEVs can effectively complement renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, by shifting their charging to align with periods of high renewable generation. For instance, when solar energy production peaks around midday, PHEVs can be programmed to charge, absorbing excess energy that might otherwise be wasted. This not only maximizes the efficiency of renewable energy systems but also minimizes the need for energy storage solutions.
- PHEVs charged during peak renewable output help stabilize the grid.
- They can mitigate energy wastage and optimize resource utilization.
- The technology supports grid resilience while integrating more renewables.
Moreover, research from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory suggests that the implementation of smart charging strategies for PHEVs can result in significant carbon emissions reductions. When consumers charge their vehicles using renewable sources, the overall carbon footprint associated with transportation decreases dramatically. This interconnection of PHEVs with renewable energy sources highlights their essential role in reducing overall emissions in the transportation sector.
Policy Support and Incentives for PHEV Adoption

Government Incentives for PHEV Buyers
- Tax rebates significantly lower the initial costs of PHEVs.
- Subsidized charging installations encourage home charging infrastructure.
- Grant programs promote innovation in PHEV technology.
Many governments recognize the importance of incentivizing the purchase of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) to encourage a move towards more sustainable transportation. Tax rebates, which can be substantial, act as a significant financial motivator for buyers. In the United States, for example, buyers can receive up to $7,500 in federal tax credits on qualifying PHEVs, making the transition much more appealing.
Furthermore, subsidies for home charging installations are increasingly common, allowing consumers to set up electrical systems at a lower cost. This not only makes owning a PHEV more convenient but also increases the likelihood of using electric power over gasoline, which dramatically decreases emissions.
Impact of Policy on Automaker Investment
The landscape for automakers has transformed significantly due to supportive policies aimed at enhancing PHEV adoption. Many manufacturers are now allocating substantial resources toward the development of plug-in hybrids because of regulatory frameworks encouraging greener technologies. A 2019 report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) noted that automaker investments in electric and hybrid technologies surged by over $300 billion.
Moreover, these policies have sparked competition among automakers to innovate and diversify their PHEV offerings. This competition not only leads to technological advancements but also results in consumers having more choices in the marketplace.
Local and Regional Support Programs
In addition to federal initiatives, local and regional governments are also playing a critical role in promoting PHEV adoption. Many cities have established unique programs tailored to their specific environmental goals, such as offering local tax credits or developing PHEV-exclusive parking spaces. Programs targeting urban areas are vital for reducing urban pollution, especially in high-density cities where traditional vehicles emit high levels of toxins.
Research from the Clean Cities Coalition indicates that areas with robust support programs see ownership rates of PHEVs increase by an average of 30%. Effective outreach and education also help consumers understand the benefits of PHEVs over conventional vehicles, further bolstering adoption.
Public Charging Infrastructure Development
The availability of public charging stations is vital for the widespread adoption of PHEVs. Without accessible charging points, many potential buyers may hesitate to switch from conventional vehicles due to concerns about charging convenience. Governments are responding by investing in charging infrastructure, with many states in the U.S. pledging millions to expand the charging network.
For instance, California's initiative to install over 1,000 public charging stations has demonstrated a positive correlation with increased PHEV sales. In conclusion, expanding charging infrastructure must go hand in hand with consumer incentives to ensure that PHEVs can be a viable option for everyone.
Future Policies and Their Implications
As the market for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles evolves, future policies will need to adapt to include more than just financial incentives. Fostering a comprehensive ecosystem that includes better energy policies, improved battery technology, and further investment in renewable energy will be crucial. Policymakers should also consider regulations that facilitate the transition of fleets to PHEV options, particularly in public transportation where emissions reductions can have a substantial impact.
With climate change becoming an increasingly urgent issue, the onus is on regulators to create a supportive environment that fosters cleaner technology. This focus could herald a time when PHEVs are no longer niche products but mainstream options for everyday use, significantly contributing to emission reduction goals.
The Future of Transportation and PHEVs

Technological Advancements Driving PHEVs
The technological advancements in Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) have significantly enhanced their efficiency and appeal. Manufacturers are constantly innovating to improve battery life, charging speeds, and overall vehicle performance. These enhancements not only cater to consumer demands for convenience but also reduce the environmental impact of each vehicle. For instance, newer models feature regenerative braking systems that recharge batteries while driving, increasing the overall electric range.
Advanced software systems are also being integrated into PHEVs. These applications provide real-time insights into energy consumption and driving behavior, enabling users to optimize their vehicle's performance based on personal habits. Such innovations underscore the ongoing evolution within the automotive sector, emphasizing sustainability and efficiency.
Government Policies Supporting PHEVs
Government incentives play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of PHEVs. Tax credits, rebates, and grants can significantly lower the initial purchase price, making these vehicles more accessible to the average consumer. In recent years, several countries have implemented policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and encouraging the transition to greener transportation methods. According to the International Energy Agency, policies supporting electric vehicle adoption have led to a marked increase in PHEV sales.
Moreover, local governments are expanding the infrastructure required for charging stations, making it easier for PHEV owners to charge their vehicles. Access to this infrastructure is a key factor in increasing consumer confidence in PHEV technology and promoting mass adoption.
Additionally, public awareness campaigns regarding the environmental benefits of PHEVs contribute to growing interest in these vehicles. Such initiatives highlight how personal choices in transportation can lead to broader environmental progress.
Environmental Impact of PHEVs
- PHEVs significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional vehicles.
- Their dual powertrain system allows for cleaner operation in urban areas.
- PHEVs contribute to reduced fossil fuel dependency.
The environmental benefits of PHEVs are increasingly recognized as a critical countermeasure to climate change. These vehicles produce lower emissions while operating in urban settings, where air quality is often a major concern. Studies have shown that PHEVs emit approximately 40% less carbon dioxide than their gasoline-powered counterparts. This reduction in emissions is vital for achieving national and global climate goals.
Furthermore, due to their hybrid technology, PHEVs can utilize electricity generated from renewable sources, further minimizing their carbon footprint. This adaptability allows PHEVs to play an essential role in transitioning away from fossil fuels and towards a more sustainable energy grid.
Challenges and Limitations Facing PHEVs
Despite the advantages of PHEVs, several challenges still impede their widespread adoption. One primary concern is the perception of limited electric range. Many consumers remain hesitant about switching from traditional vehicles due to fears of running out of battery power mid-trip. While recent models have improved in this aspect, educating potential buyers about the hybrid functionality is crucial.
Another challenge is the varying availability of charging infrastructure. In rural areas, charging stations may be sparse, discouraging potential purchasers. Efforts are being made to expand charging networks, particularly in less populated regions, but comprehensive coverage remains a significant hurdle to PHEV expansion.
Additionally, the initial purchase price of PHEVs can be higher than that of conventional cars. Although long-term savings can be achieved through fuel savings and lower maintenance costs, the upfront investment may still deter some buyers. Government incentives can help, but public policy must continue to evolve to embrace PHEV technology fully.
The Future of PHEVs in Urban Mobility
As urban centers continue to grow, the need for sustainable transportation solutions becomes even more pressing. PHEVs are well-suited for urban mobility due to their flexibility and efficiency in short-distance travel. Many cities are adopting stricter emissions regulations, further enhancing the appeal of PHEVs as environmentally-friendly alternatives.
Furthermore, as battery technology continues to advance, future PHEVs are set to feature increased range and faster charging capabilities. Innovations in energy storage are paving the way for longer battery life, which could alleviate consumer concerns regarding range anxiety. By integrating smart grid technology, PHEVs could also enable better energy management systems, allowing for efficient energy distribution during peak hours.
Ultimately, the future of PHEVs looks promising as they align with broader trends in sustainable transportation and technology. Their continued development will likely coincide with growing urban populations and a heightened focus on eco-friendly transit solutions.





