Regional Differences in EV Incentives and Rebates
Incentivizing Electric Vehicle Adoption
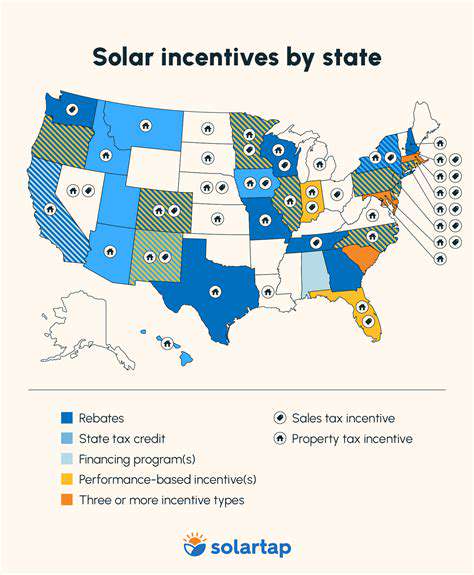
State-level incentives play a crucial role in driving the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). These incentives, which can include tax credits, rebates, or reduced registration fees, are designed to offset the higher upfront cost of EVs compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. By making EVs more affordable, states aim to encourage greater consumer demand and accelerate the transition to a cleaner transportation system. These programs vary significantly across the United States, reflecting differing priorities and resources.
While some states offer comprehensive packages of incentives, others may focus on specific aspects of EV ownership, such as charging infrastructure or vehicle purchase. Understanding these differences is critical for potential EV buyers, allowing them to make informed decisions about where to purchase and utilize their electric vehicles. The availability and structure of incentives can significantly impact the overall appeal of EVs in different regions.
Varying Approaches to Incentives
The approaches to incentivizing EV adoption are quite diverse. Some states provide significant tax credits, potentially reducing the price of an EV by a substantial amount. Other states may offer rebates upon the purchase of an EV, providing a one-time financial benefit. These diverse approaches often reflect the unique economic conditions and policy priorities of each state. Furthermore, some states offer incentives tied to the specific characteristics of the EV, such as the battery capacity or the manufacturer's reputation for environmental responsibility.
The goal of these incentives is generally to stimulate the market for electric vehicles and to encourage a shift away from traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles. Incentives can also be tied to the creation of charging stations, recognizing the importance of infrastructure in supporting EV adoption. These strategies are often tailored to address specific challenges or opportunities within each state.
Geographic Differences and Impact
The geographic distribution of EV incentives highlights the varying priorities of different states. Some states with a strong commitment to environmental sustainability tend to offer more substantial incentives than those with less pronounced environmental policies. This disparity in incentives can lead to significant variations in the cost of electric vehicles across the country. The availability of incentives is a key factor in determining the overall appeal of EVs in different regions and impacts the EV market.
Moreover, the effectiveness of incentives is often measured by the impact they have on sales figures and the adoption rate of EVs. Tracking these statistics can provide valuable insights into the success of various approaches and inform future policy decisions. Ultimately, the interplay of state-level incentives, consumer demand, and technological advancements will shape the future of electric vehicle adoption in America.
Federal Incentives: A National Framework with Regional Applications
Incentivizing Investment in Renewable Energy
Federal incentives for renewable energy projects are crucial for driving a national transition to cleaner energy sources. These incentives, which can take the form of tax credits, grants, and streamlined permitting processes, are designed to mitigate the financial risks associated with renewable energy development. Understanding the specific types of incentives available and how they are applied is paramount for attracting investment in renewable energy projects, particularly in regions with strong renewable energy potential.
Regional variations in renewable energy resources, such as solar irradiance or wind speeds, can significantly impact the effectiveness of federal incentives. For example, a region with abundant solar resources might benefit more from tax credits for solar panel installations, while a region with strong wind resources might see greater returns from incentives for wind turbine construction.
Streamlining Permitting Processes
Bureaucratic hurdles and lengthy permitting processes can significantly hinder the development of renewable energy projects. Federal incentives, therefore, often include provisions to streamline these processes. This includes expediting environmental impact assessments and simplifying permitting requirements for projects that align with national renewable energy goals. However, regional variations in environmental regulations and permitting agencies can still present challenges.
The federal government can play a vital role in harmonizing regional permitting practices, ensuring that the implementation of incentives is consistent across different jurisdictions. This will ensure projects can move forward efficiently and effectively.
Tax Credits and Grants for Energy Efficiency
Federal incentives can also target energy efficiency improvements in existing buildings and infrastructure. These incentives can include tax credits for homeowners and businesses that invest in energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and other upgrades. Such incentives can encourage the adoption of energy-saving technologies, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions, particularly in regions with higher energy costs.
Regional Variations in Energy Needs and Resources
The effectiveness of federal incentives often depends on a deep understanding of regional differences in energy needs and resource availability. Regions with high energy demands might benefit from incentives that encourage the development of large-scale renewable energy projects, while regions with abundant renewable resources might need incentives that encourage the efficient use and storage of those resources.
Financial Assistance for Community-Based Projects
Federal incentives can also play a role in supporting community-based renewable energy projects, which can be critical for ensuring equitable access to clean energy in underserved regions. These projects often require innovative financing mechanisms and tailored support systems, and federal incentives can help bridge the gap between project development and implementation. This support is particularly relevant in areas with lower economic development and where community engagement is vital.
Infrastructure Development and Grid Modernization
Federal incentives can be crucial for modernizing electricity grids and developing the necessary infrastructure to accommodate the integration of renewable energy sources. This includes investments in smart grids, energy storage solutions, and transmission lines. Regional differences in grid infrastructure and technological needs should be carefully considered when designing and implementing these incentives to ensure that they address specific regional challenges effectively.
Economic Impact and Job Creation
Federal incentives for renewable energy can generate significant economic benefits, creating jobs and boosting economic activity across various sectors. These incentives are often designed to stimulate investment and development in renewable energy technologies, leading to the creation of new industries and the expansion of existing ones. Regional disparities in economic development should be factored into the design of incentives to ensure that the benefits are distributed equitably.
State-Level Variations: A Patchwork of Policies
State-Level Funding Disparities
Significant discrepancies exist in state-level funding models for crucial public services, impacting the quality and accessibility of education, healthcare, and social welfare programs. These variations are often rooted in historical factors, differing economic conditions, and varying political priorities. Understanding these disparities is critical to crafting effective policy solutions at the national level. Different states have dramatically different capacities to provide vital services to their citizens, leading to uneven outcomes and opportunities across the nation. These variations often highlight the need for more equitable resource allocation strategies.
The consequences of these funding gaps are far-reaching, impacting everything from student achievement to life expectancy rates. For example, states with limited funding may struggle to maintain adequate teacher salaries, leading to high turnover rates and decreased educational quality. This, in turn, can have a ripple effect on future economic development and opportunity within the state. This reinforces the importance of considering the interconnectedness of state-level policies and their national implications.
Impact on Public Service Provision
State-level variations in funding profoundly affect the availability and quality of public services. This includes disparities in infrastructure development, environmental protection, and public safety initiatives. For instance, states with robust funding often boast modern infrastructure, leading to improved transportation systems, enhanced communication networks, and more efficient emergency response capabilities. Conversely, states with limited resources may face challenges in maintaining existing infrastructure and implementing new initiatives.
These discrepancies in funding can lead to major inequities in service provision. This can translate into disparities in access to quality healthcare, educational opportunities, and social support networks. Addressing these disparities necessitates a comprehensive approach that considers the unique needs and contexts of each state. This includes identifying the root causes of these funding differences and developing targeted solutions to promote equity and fairness.
Furthermore, the lack of uniformity in funding models can hinder the development of national standards and benchmarks for public services. This makes it difficult to measure effectiveness and identify best practices. This lack of comparable data can also make it challenging to evaluate the overall impact of policy interventions on a national scale.
Policy Implications and Solutions
The observed variations in state-level funding highlight the need for a nuanced approach to public policy at both the state and national levels. Developing solutions that are sensitive to the unique needs of each state is crucial. This requires ongoing data collection and analysis to understand the factors driving these disparities.
One potential solution lies in exploring more equitable funding mechanisms at the federal level. This might include national grants or matching funds to support states with lower levels of funding. However, such solutions must be carefully designed to avoid unintended consequences and to ensure that funding is allocated fairly and effectively. Another approach involves leveraging existing resources and partnerships to maximize impact. This includes fostering collaboration among states, organizations, and communities to share best practices and expertise.
Ultimately, bridging these funding gaps requires a commitment to collaboration, innovation, and a shared understanding of the importance of equitable access to quality public services. This will ensure that all citizens, regardless of their state of residence, have access to essential resources and opportunities that foster a healthy, thriving, and equitable society.
Read more about Regional Differences in EV Incentives and Rebates
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies