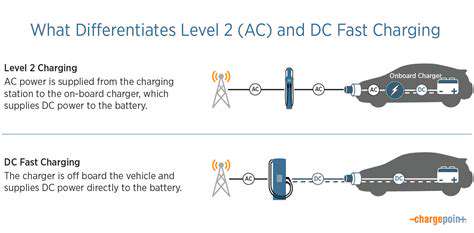
Robotics for Cross Docking Operations: Speeding Up Transit
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): Revolutionizing Warehouse Operations
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are transforming warehouse operations by automating material handling and logistics. Their ability to navigate complex warehouse environments without human intervention significantly improves efficiency and reduces labor costs. This automation allows for optimized workflows, leading to faster order fulfillment and increased throughput. AMRs are particularly well-suited for repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on higher-value activities.
AMR Navigation Technologies: Precision and Safety
AMRs utilize advanced navigation technologies, including laser scanners, cameras, and sophisticated algorithms, to precisely map and navigate warehouse layouts. These technologies enable AMRs to avoid obstacles, identify designated locations, and accurately deliver goods. Safety features are crucial, and AMRs are equipped with sensors and collision avoidance systems to ensure safe operation within the warehouse environment, minimizing the risk of accidents and damage to goods.
Warehouse Integration and Workflow Optimization
Effective integration of AMRs into existing warehouse systems is critical for maximizing their benefits. This involves seamless communication with warehouse management systems (WMS) to coordinate tasks, track inventory, and optimize routes. Integrating AMRs with existing workflows allows for a smooth transition, minimizing disruptions and maximizing productivity. Proper integration leads to a more streamlined and efficient overall warehouse operation.
Benefits of AMR Implementation: Cost Savings and Efficiency
Implementing AMRs in warehouses yields significant cost savings and operational efficiencies. Automation reduces labor costs, minimizes errors associated with manual handling, and accelerates order fulfillment. AMRs can work 24/7, increasing overall throughput and providing a consistent level of service. This increased efficiency translates into significant cost savings over time, making AMRs a worthwhile investment for modern warehouses.
AMR Types and Applications: Tailored Solutions for Diverse Needs
AMRs come in various types, each designed for specific warehouse applications. Some AMRs specialize in carrying heavy loads, while others are designed for picking and packing tasks. This diversity allows for tailored solutions that cater to the unique needs of different warehouses. AMRs can be deployed for a wide range of tasks, including transporting goods between different areas of a warehouse, picking items from shelves, and delivering orders to designated locations.
Future Trends in AMR Technology and Development
Future developments in AMR technology are expected to push the boundaries of automation in warehouse operations. Improvements in navigation, communication, and artificial intelligence (AI) will lead to even greater efficiency and flexibility. Advancements in AI will enable AMRs to learn and adapt to changing warehouse conditions, further optimizing their performance and capabilities. The integration of more advanced sensors and AI algorithms will create even safer and more intelligent warehouse environments.
Challenges and Considerations in AMR Implementation
While AMRs offer significant advantages, implementing them in a warehouse presents certain challenges. These include the cost of initial investment, the need for careful planning and integration into existing systems, and the potential need for retraining of warehouse staff. Careful consideration of these challenges is essential for a successful implementation. It is crucial to assess the specific needs of the warehouse and select the appropriate AMR technology and implementation strategy to ensure maximum benefit.
Future Trends and Considerations

Technological Advancements Shaping the Future
Rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are poised to revolutionize various sectors, impacting everything from healthcare and manufacturing to customer service and transportation. AI-powered tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling automation of complex tasks and potentially leading to unprecedented levels of efficiency and productivity. This shift will undoubtedly require workforce adaptation and potentially lead to new job opportunities in areas like AI development and maintenance.
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) is also transforming how we interact with the world around us. Connected devices are becoming more prevalent, collecting and analyzing data to improve efficiency and create new possibilities for personalized experiences. This interconnectedness promises significant benefits across industries, including smart homes, intelligent transportation systems, and optimized agricultural practices. However, concerns about data security and privacy need careful consideration in this increasingly data-driven world.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Environmental consciousness is driving a growing demand for sustainable practices across industries. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly manufacturing processes, implementing renewable energy sources, and focusing on reducing their carbon footprint. This trend is not only driven by ethical considerations but also by the need to comply with stricter environmental regulations and meet consumer demands for sustainable products.
The need to address climate change is paramount. Innovative solutions are emerging in areas like carbon capture and storage, renewable energy technologies, and sustainable agriculture. This necessitates a global collaboration to mitigate the risks associated with environmental degradation and foster a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Economic Shifts and Global Interdependence
Globalization continues to reshape the global economy, driving increased interdependence among nations. International trade and investment are creating new opportunities for economic growth and development, but also pose challenges related to supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions. Understanding and addressing these complexities will be critical for navigating the evolving global landscape.
The increasing prevalence of remote work and virtual collaboration is transforming business models and workforces. Adapting to these changes requires a focus on flexible work arrangements, robust communication technologies, and strategies for effective remote team management. This shift towards greater flexibility is likely to continue and shape the future of work in significant ways.
Social Impact and Ethical Considerations
The growing influence of social media and digital platforms raises important ethical considerations regarding privacy, misinformation, and the potential for manipulation. Safeguarding individual privacy and combating the spread of harmful content are crucial for maintaining a healthy and informed online environment. A greater emphasis on digital literacy and media literacy will be essential for empowering individuals to navigate this complex digital landscape.
The increasing use of AI in decision-making processes raises concerns about bias and fairness. Ensuring equitable access to technology and minimizing potential biases in algorithms will be crucial for building a just and inclusive society. Developing ethical guidelines and regulations for the responsible use of AI is becoming increasingly important to mitigate potential harms and maximize benefits.
Emerging Technologies and Innovation
The future is full of exciting possibilities, with emerging technologies like advanced materials, biotechnology, and quantum computing poised to revolutionize various sectors. These innovations hold the potential to solve critical global challenges and create new opportunities for economic growth and societal advancement. The rapid pace of technological advancement requires continuous adaptation and a focus on fostering innovation to stay ahead of the curve.
Space exploration and colonization are becoming more than just scientific pursuits. The development of sustainable space infrastructure and the potential for resource extraction in space represent a frontier of innovation with significant economic and geopolitical implications. These ventures could also potentially provide answers to pressing issues on Earth and lay the groundwork for a more sustainable and resilient future.
Read more about Robotics for Cross Docking Operations: Speeding Up Transit
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies