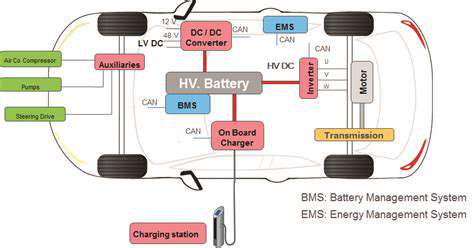
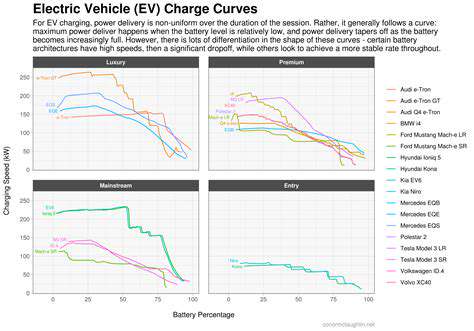
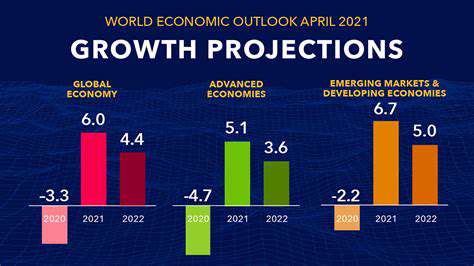
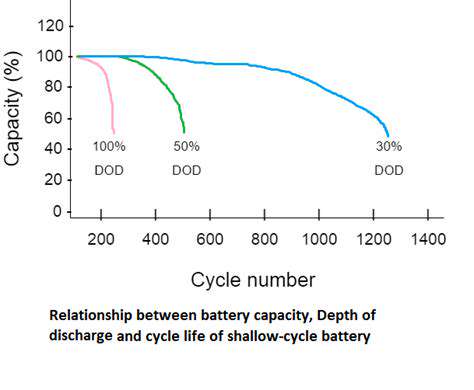
Small Modular Nuclear Reactors (SMRs): A Complementary Role in Decarbonization?
Introduction to Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
What are Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)?
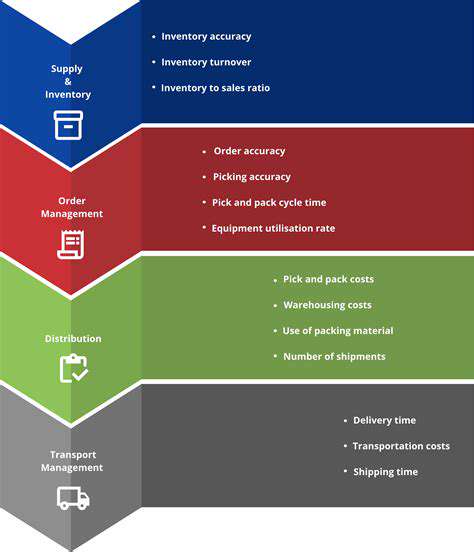
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are nuclear reactors designed to be smaller and more modular than traditional large-scale nuclear power plants. This modularity allows for easier and faster deployment, potentially reducing construction time and costs. They are designed with safety and enhanced security features in mind, playing a crucial role in the advancement of nuclear energy technology. SMRs offer a compelling alternative for addressing the global energy demands while contributing to a sustainable future.
These smaller reactors can be factory-fabricated in a controlled environment, leading to higher quality control and potentially lower construction costs compared to traditional, large-scale plants. This standardized approach also facilitates easier maintenance and replacement of components, which can help minimize downtime and maximize operational efficiency.
Key Benefits of SMR Technology
One significant advantage of SMRs is their potential for faster deployment. The modular design allows for the construction of multiple units in parallel, significantly reducing the overall time needed to bring new power generation capacity online. This can be crucial for countries or regions facing immediate energy needs and infrastructure challenges.
SMRs also present a compelling economic case. Their smaller size and factory-based construction methods can result in lower initial capital costs. Furthermore, the modular approach can lead to economies of scale in manufacturing, potentially further reducing the cost per kilowatt of electricity generated.
Safety and Security Considerations
Safety is paramount in nuclear power, and SMRs are designed with advanced safety features to mitigate potential risks. These include passive safety systems that rely on natural forces like gravity and convection to respond to malfunctions, reducing the need for active interventions and ensuring reactor stability. Advanced security measures are also integrated to prevent unauthorized access and malicious acts.
Environmental Impact of SMRs
SMRs aim to reduce the environmental footprint of nuclear power generation. Their smaller size and modular design can lead to lower land use compared to larger plants. Furthermore, the factory-based construction methods can minimize the environmental impact associated with traditional construction activities on-site. The use of advanced technologies in SMR design can also enhance operational efficiency and minimize waste generation.
Future Applications and Potential Market
The potential applications of SMRs extend beyond traditional power generation. They could potentially be used in remote areas, for example, to provide reliable power to communities or industries where grid access is limited. The modular design also opens up possibilities for applications like district heating and desalination plants.
SMRs are expected to play an increasingly important role in the global energy market. Their ability to be deployed more quickly and affordably compared to large-scale plants, combined with their advanced safety features, positions them for significant growth in the coming years.
Technological Advancements Driving SMR Development
Continuous advancements in materials science, reactor design, and control systems are driving the development of more efficient and safe SMRs. These advancements contribute to improved performance, enhanced safety features, and reduced operational costs. The ongoing research and development efforts are crucial for optimizing SMR technology and unlocking its full potential in the future.
Innovations in reactor core design and fuel management are leading to improved efficiency and reduced waste generation. These advancements are critical to ensure that SMRs meet the stringent environmental and safety standards of the future.

SMRs as a Component of a Diverse Energy Portfolio

SMRs and the Importance of Diversity in the Workplace
Understanding and implementing strategies for creating a diverse and inclusive workplace is critical for organizations seeking to thrive in today's global environment. A diverse workforce brings a multitude of perspectives, experiences, and ideas, which can lead to increased innovation and creativity. This diversity fosters a more inclusive environment where employees feel valued and respected, ultimately leading to higher levels of engagement and productivity.
Focusing on specific segments of the population, like those belonging to underrepresented groups, is essential. When companies actively work to create a welcoming and equitable environment for everyone, they unlock the full potential of their employees and contribute to a more positive and productive workplace culture.
Strategic Management of Resources (SMRs) and their Role
Strategic Management of Resources (SMRs) can play a crucial role in supporting the development and implementation of diversity and inclusion initiatives within an organization. SMRs encompass the planning, organizing, and managing of resources to achieve specific goals and objectives. When these resources are allocated effectively, they can significantly contribute to building a more inclusive and diverse workforce.
By focusing on areas such as recruitment, training, and promotion, SMRs can help create a pathway for underrepresented groups to advance within the company. This ensures that diverse voices are heard and valued at all levels of the organization.
Specific Applications of SMRs in Diverse Environments
SMRs can be applied in various ways to support diversity and inclusion efforts. One key application is in developing targeted recruitment strategies that actively seek out candidates from underrepresented groups. This proactive approach can help address imbalances in representation and create a more diverse talent pool.
Another application involves providing specialized training programs to help employees from all backgrounds understand and appreciate different perspectives. These programs can foster an inclusive environment where everyone feels comfortable sharing their ideas and collaborating effectively.
Measuring the Impact of SMRs on Diversity
Measuring the impact of SMRs on diversity and inclusion is crucial for understanding their effectiveness. Organizations can track key metrics such as representation of underrepresented groups in different roles and levels within the company, employee satisfaction and engagement data, and feedback from employees about their experiences in the workplace.
Analyzing these data points can provide valuable insights into areas where the SMRs need adjustments or improvements to better support diversity and inclusion goals. Regular evaluation and refinement of SMRs are critical to ensure that they continue to drive positive change within the organization.
The Future of SMRs and Diversity Initiatives
As the importance of diversity and inclusion continues to grow, SMRs will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the workplace. Organizations will need to continually adapt and evolve their SMRs to reflect the changing needs of a diverse workforce and to remain competitive in the global market.
By prioritizing diversity and inclusion, companies will not only create a more equitable and welcoming environment for their employees but also unlock new opportunities for innovation, creativity, and success.
Read more about Small Modular Nuclear Reactors (SMRs): A Complementary Role in Decarbonization?
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies