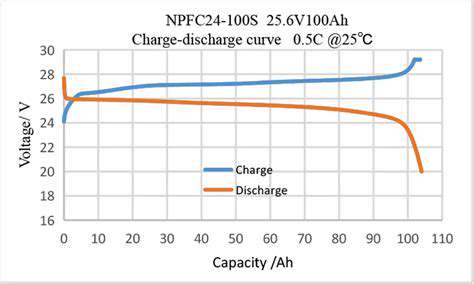
Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
Optimizing Crop Production Under Solar Panels

Environmental Benefits and Economic Viability
Environmental Benefits of Agrivoltaics
Agrivoltaics, a system that integrates solar photovoltaic panels with agricultural land use, offers a multitude of environmental benefits. By utilizing otherwise idle land for solar energy generation, agrivoltaics reduces the pressure on natural ecosystems and landscapes. This innovative approach minimizes the need for new land conversion, preserving valuable habitats and biodiversity. The shade provided by the solar panels can also benefit certain crops, moderating temperatures and reducing water stress, leading to potentially increased yields and resilience to climate change.
Furthermore, the reduced need for pesticides and herbicides in shaded areas can promote healthier soil ecosystems and support a more sustainable agricultural practice. This can lead to a reduction in harmful runoff into water sources, improving water quality and protecting aquatic ecosystems. The overall environmental impact of agrivoltaics is positive, as it combines renewable energy generation with sustainable agricultural practices, creating a win-win scenario for both the environment and human needs.
Economic Viability of Agrivoltaics
The economic viability of agrivoltaics hinges on several factors, including the cost of land, the price of solar panels, and the market value of the agricultural products. While the initial investment can be substantial, the long-term economic benefits often outweigh the upfront costs. The integration of solar panels with agriculture can increase land value, providing a significant return on investment over time. Additionally, the generation of renewable energy can lead to lower energy costs for farmers, reducing operational expenses and improving the financial stability of the agricultural enterprise.
The added value of shade-tolerant crops and the potential for increased yields can contribute to the overall profitability of the agrivoltaic system. Furthermore, the growing demand for renewable energy and government incentives for sustainable practices can further enhance the economic viability of agrivoltaics, creating a supportive environment for its wider adoption. The potential for diversification of income streams, from both solar energy and agricultural products, strengthens the long-term economic benefits of this dual-use land approach.
Maximizing Synergies and Challenges
Successfully implementing agrivoltaic systems requires careful consideration of maximizing the synergistic benefits between solar energy generation and agricultural production. Optimizing crop selection based on shade tolerance and the specific microclimate created by the panels is crucial to ensure both high crop yields and efficient solar energy capture. Careful planning and design are essential to mitigate potential challenges, such as the potential impact of panels on water and nutrient availability and the need for appropriate infrastructure for maintenance and access.
Challenges in achieving widespread adoption include the cost of initial setup, the need for customized designs to suit diverse agricultural settings, and the need for supportive policies and incentives to encourage investment. Addressing these challenges through research, development, and policy initiatives is key to unlocking the full potential of agrivoltaics as a sustainable and economically viable solution for meeting both energy and food security needs. Overcoming these challenges can pave the way for a future where agrivoltaics plays a significant role in the transition to a more sustainable and resilient agricultural and energy sector.
Technological Advancements and Future Prospects

Technological Advancements in Communication
The rapid evolution of communication technologies has revolutionized the way we interact, share information, and conduct business. From the invention of the telephone to the advent of the internet and mobile devices, each advancement has dramatically altered human communication patterns. This constant evolution has led to a more interconnected and globalized world, facilitating instant communication across vast distances.
The rise of social media platforms has further accelerated this trend, enabling individuals to connect with others on a global scale. This interconnectedness, while offering numerous benefits, also presents new challenges, such as the spread of misinformation and the potential for cyberbullying. Furthermore, the constant barrage of information can be overwhelming, necessitating critical thinking skills to discern reliable sources from unreliable ones.
Impact on Industries
Technological advancements are profoundly impacting various industries, driving innovation and productivity gains. Automation and artificial intelligence are transforming manufacturing, logistics, and customer service, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings. This automation, while beneficial in many ways, also raises concerns about job displacement and the need for workforce retraining.
Healthcare Innovations
The healthcare sector has been significantly transformed by technological advancements. Medical imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans, along with robotic surgery, are enhancing diagnostic capabilities and surgical precision. Furthermore, the development of sophisticated medical devices and personalized medicine approaches are improving patient outcomes and extending lifespans.
These advancements are not only improving the quality of care but also making healthcare more accessible and affordable in many parts of the world. However, ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and the equitable distribution of these technologies remain crucial issues to address.
Environmental Sustainability
Technological innovation is playing a critical role in addressing environmental challenges. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are becoming increasingly cost-effective and efficient, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. This shift towards cleaner energy is essential for mitigating climate change and reducing our environmental footprint.
Advanced materials and technologies are also contributing to more sustainable manufacturing processes and waste management strategies. However, the transition to a sustainable future requires significant investment in research, development, and infrastructure, as well as a global commitment to collaborative efforts.
The Future of Work
Technological advancements are reshaping the future of work, demanding adaptability and continuous learning from employees across all industries. New roles and responsibilities are emerging, requiring individuals to acquire new skills and knowledge to remain competitive in the workforce.
The rise of remote work and flexible work arrangements is changing the traditional office environment. Moreover, automation and AI are impacting the nature of work, potentially leading to job displacement in certain sectors. Ultimately, the future of work requires a proactive approach to upskilling and reskilling to ensure that individuals are equipped to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Ethical Considerations
Technological advancements often raise complex ethical considerations that require careful examination. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential misuse of technology need careful consideration and regulatory frameworks. Ensuring responsible innovation is paramount to harnessing the benefits of technology while mitigating potential harms. The development of ethical guidelines and policies is essential for navigating the complex ethical landscape created by technological progress.
Furthermore, ensuring equitable access to these advancements and their benefits for all members of society is a critical ethical imperative. This involves addressing potential disparities and promoting inclusivity in the design and implementation of new technologies.
Global Impact
Technological advancements are having a profound global impact, connecting communities, and fostering cross-cultural understanding. Globalization is accelerating, leading to the exchange of ideas, goods, and services across international borders. The spread of information and communication technologies is empowering individuals and communities in diverse parts of the world.
However, these advancements also present challenges related to cultural sensitivity, global inequalities, and the potential for the misuse of technology for malicious purposes. Addressing these challenges requires a global approach to promoting ethical and responsible technological advancement.
The Role of Policy and Support Systems

The Importance of Policy Frameworks
Effective policy frameworks are crucial for fostering a supportive environment for innovation and growth. These frameworks act as a guiding compass, providing clear direction and incentives for individuals and organizations to pursue ambitious projects and initiatives. A well-defined policy framework ensures that resources are allocated strategically, maximizing their impact on desired outcomes. Policies should be adaptable and responsive to changing societal needs and technological advancements, fostering a dynamic and resilient ecosystem.
Clear policy directives can also mitigate potential risks and uncertainties, creating a sense of stability and predictability. This predictability is essential for attracting investment, both domestic and international, and encouraging entrepreneurial endeavors. By outlining clear expectations and responsibilities, policies create a level playing field, promoting fair competition and collaboration.
Strategic Support Systems
Robust support systems are essential for nurturing innovation and ensuring its successful implementation. These systems encompass a wide range of services, including access to funding, mentorship, networking opportunities, and training programs. Access to these resources is particularly critical for startups and small businesses, which often lack the internal infrastructure to navigate the complexities of the market.
Mentorship programs play a vital role in guiding entrepreneurs through the challenges of starting and scaling businesses. Mentors can provide valuable insights, practical advice, and support networks, ultimately accelerating the growth trajectory of businesses and increasing their chances of success. Mentors can offer invaluable experience and knowledge, helping startups avoid common pitfalls. This support is crucial to bridge the gap between vision and execution.
Financial Incentives and Funding Opportunities
Financial incentives and access to funding are critical components of effective support systems. Government grants, tax breaks, and low-interest loans can provide significant financial relief for businesses, especially during their early stages. This financial support can help businesses overcome significant hurdles and accelerate their growth trajectory.
Access to venture capital and angel investors is also crucial for scaling businesses. These investors provide not just capital but also valuable industry connections and expertise. These financial opportunities are often the deciding factor in whether a startup can achieve its long-term goals and become a sustainable and profitable entity.
Networking and Collaboration Platforms
Facilitating networking and collaboration among stakeholders is essential for fostering innovation. Platforms that connect researchers, entrepreneurs, investors, and policymakers can accelerate the exchange of ideas and knowledge, leading to breakthroughs and advancements. These connections can spark collaborative projects and innovative solutions that benefit society as a whole.
Industry events, conferences, and workshops provide valuable opportunities for networking and knowledge sharing. These events can bring together individuals from diverse backgrounds, fostering cross-sector collaborations and partnerships. Networking is critical for establishing relationships that can lead to future collaborations and support.
Education and Skill Development Initiatives
Investing in education and skill development is vital for building a skilled workforce capable of driving innovation. This includes providing access to relevant training programs, courses, and educational resources. This ensures that individuals possess the necessary skills to thrive in a rapidly evolving economy.
Upskilling and reskilling initiatives are particularly important in the face of technological advancements. These initiatives help workers adapt to new technologies and industries, ensuring that they remain relevant and competitive in the job market. Continuous education is crucial for individuals to maintain their competitiveness and adapt to changing industry demands.
Read more about Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies