Top Tips for Maintaining EV Battery Health
Optimizing EV Battery Longevity Through Smart Practices
Mindful Driving: Protecting Your Battery's Core
The Science Behind Battery Wear
Modern electric vehicles rely on sophisticated battery systems that respond differently than combustion engines to driving patterns. These power sources experience gradual wear influenced by multiple variables, with driver behavior ranking among the most significant. Unlike sudden mechanical failures, battery degradation occurs incrementally through chemical changes within the cells.
Temperature extremes represent one of the most aggressive battery stressors. Both scorching heat and freezing cold trigger undesirable electrochemical reactions that compromise cell integrity. Thoughtful driving and charging routines can dramatically reduce exposure to these damaging conditions, directly impacting the battery's service life.
The Hidden Cost of Quick Charging
While rapid charging stations offer undeniable convenience, they impose substantial thermal stress on battery packs. The intense electrical currents required for fast charging generate excessive heat that degrades internal components over time. This thermal punishment gradually erodes the battery's energy storage capacity and overall performance metrics.
Strategic charging choices make a measurable difference. Prioritizing standard charging speeds for routine use preserves cell health, reserving fast charging for essential situations. This balanced approach maintains practicality while protecting your investment in electric mobility.
Smooth Operation Principles
Progressive acceleration and anticipatory braking significantly reduce battery strain. Sudden power demands force the battery to deliver extreme current loads, creating internal heat buildup that accelerates chemical breakdown. Similarly, abrupt deceleration through harsh braking generates recoverable energy but at the cost of additional thermal stress.
Charge Cycle Management
Consistent charging habits form the foundation of battery preservation. Allowing complete discharge or frequently cycling between full and empty states creates unnecessary stress on the electrochemical system. Maintaining charge levels between 20-80% for daily use proves ideal for most lithium-ion batteries, though specific manufacturer guidelines should take precedence.
This charging strategy minimizes the expansion and contraction of battery materials that occurs during deep cycling. By reducing these physical stresses, owners can expect extended service life and more consistent performance throughout the battery's lifespan.
Irish stew, that iconic comfort food, represents far more than basic sustenance. This culinary tradition carries centuries of Irish heritage in its preparation, showcasing how simple ingredients transform into profound nourishment through patient cooking. Beyond mere nutrition, it offers a direct connection to cultural identity and shared history.
Proactive Battery Care Strategies
Essential Maintenance Routines
Systematic maintenance represents the most effective method for preserving battery capacity and reliability. These preventive measures help avoid premature aging and unexpected power failures that could leave you stranded. The cumulative effect of proper care translates to significant long-term savings and uninterrupted operation.
Terminal maintenance often gets overlooked despite its importance. Oxidation buildup on electrical contacts increases resistance, reducing charging efficiency and power delivery. A periodic cleaning with appropriate materials maintains optimal conductivity throughout the vehicle's electrical system.
Health Monitoring Techniques
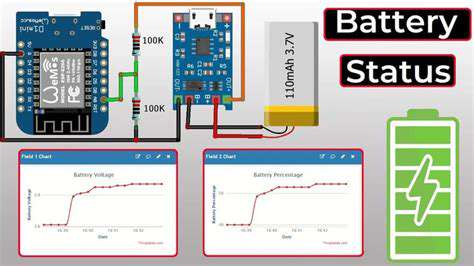
Modern EVs provide numerous tools for tracking battery condition. Learning to interpret state-of-health metrics allows owners to detect emerging issues before they become serious problems. Many systems track historical data that reveals subtle degradation patterns invisible during normal operation.
Tracking charge cycle counts and capacity retention provides the clearest picture of battery condition. Sudden changes in these metrics often indicate the need for professional evaluation, potentially catching issues while they remain manageable through software recalibration or minor component replacement.
Optimal Charging Protocols
Charging practices significantly influence battery longevity. Using manufacturer-approved equipment ensures proper voltage regulation and current control during the charging process. Third-party chargers might save money initially but often lack the sophisticated management systems that protect battery health.
The practice of maintaining partial charge states proves particularly beneficial for lithium-ion chemistry. While full charges are necessary for maximum range trips, daily charging to 80-90% capacity reduces electrode stress compared to repeated 100% charges. Many EVs now include charge limit settings to automate this protection.
Environmental Protection Measures
Batteries react strongly to their thermal environment. Prolonged exposure to temperatures outside the ideal 15-25°C (59-77°F) range accelerates chemical degradation. Parking in shaded areas during summer and using climate-controlled storage in winter can dramatically slow this aging process.
Storage Best Practices
Extended storage requires special consideration to prevent capacity loss. The ideal storage charge level varies by battery chemistry but typically falls between 40-60% for lithium-ion systems. This charge state minimizes chemical activity while preventing damaging deep discharge that can occur during inactivity.
Storage location selection impacts long-term preservation more than most owners realize. Temperature-stable environments like interior garages outperform exterior parking for maintaining battery health. For seasonal storage, periodic charging to maintain the ideal storage level prevents self-discharge from draining the battery completely.

Read more about Top Tips for Maintaining EV Battery Health
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies