Decentralization of Energy Generation in Smart Homes
Renewable Energy Integration: A Sustainable Path Forward

Renewable Energy Integration: Challenges and Opportunities
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges for the energy sector. Transitioning to a more sustainable energy future hinges on effectively integrating these intermittent sources into existing grids, ensuring reliability and stability. This requires innovative solutions to address the fluctuating nature of renewable energy production and the need for grid modernization.
Efficient energy storage technologies are crucial for managing the variability of renewable energy generation. Solutions like pumped hydro, battery storage, and advanced thermal storage systems are critical to balancing supply and demand. Further development and deployment of these technologies will be essential for a reliable and sustainable energy grid.
Addressing Intermittency and Grid Stability
A key challenge in integrating renewables is their inherent intermittency. Solar and wind power generation fluctuate depending on weather conditions, which can lead to imbalances in supply and demand. This necessitates robust grid management strategies to maintain grid stability. Advanced forecasting technologies and smart grid technologies are vital to anticipate fluctuations and adjust energy distribution accordingly.
Transmission and distribution infrastructure often needs upgrades to accommodate the influx of renewable energy. This includes strengthening existing networks and potentially developing new transmission lines to connect renewable energy sources to consumption centers. Investing in these upgrades is essential for ensuring the efficient and reliable transport of renewable energy.
Effective grid management systems are essential to address the intermittency of renewable energy sources. These systems need to be able to accurately forecast energy production, manage energy storage, and dynamically adjust energy distribution to meet demand. Real-time data analysis and intelligent control algorithms are crucial for achieving this.
Smart grid technologies play a critical role in optimizing energy flow and managing the integration of renewable energy sources. These technologies can monitor energy consumption patterns, predict future demand, and automatically adjust power distribution to maintain grid stability.
Policy and Economic Factors
Government policies and incentives play a significant role in driving the integration of renewable energy. Supportive policies, such as feed-in tariffs and renewable portfolio standards, can incentivize investment in renewable energy projects. These policies can also help to overcome financial barriers and support the transition to a clean energy future.
The economic viability of renewable energy projects is also influenced by factors such as technological advancements, resource availability, and grid infrastructure development. These factors need to be carefully considered when developing policies and strategies for renewable energy integration. Economic incentives and subsidies can play a vital role in encouraging private sector investment and accelerating the transition.
The cost of renewable energy technologies is continually decreasing, making them increasingly competitive with traditional fossil fuels. However, integrating these technologies into existing energy systems requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure upgrades and supportive policies.
Mean reversion is a fundamental concept in finance that posits that asset prices, over the long term, tend to revert to their historical average or mean. This implies that assets that have experienced significant price increases are likely to experience a subsequent decline, and vice versa. Understanding the concept of mean reversion is crucial for investors, as it can help them to identify potential opportunities and manage risk effectively. A key aspect of mean reversion is the recognition that while markets can experience periods of significant volatility and deviation from the mean, the underlying tendency is towards the long-term average.
Energy Storage Solutions: Enhancing Grid Stability
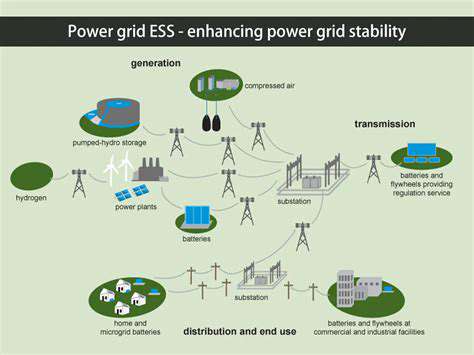
Energy Storage Fundamentals
Energy storage solutions are crucial for a sustainable energy future, enabling us to harness intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind. These systems essentially capture excess energy generated during peak production and release it when demand is high, smoothing out the supply and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Understanding the fundamental principles behind these systems is vital for developing effective and efficient solutions.
Various technologies are employed in energy storage, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. From pumped hydro storage, which leverages gravity to store energy in elevated reservoirs, to batteries, which use electrochemical reactions, the diverse range of options allows us to tailor solutions to specific needs and contexts. This diverse range of technologies offers a multitude of choices for different applications.
Battery Technology Advancements
Battery technology is rapidly evolving, with advancements in materials and designs leading to increased energy density, longer lifespans, and reduced costs. Lithium-ion batteries are currently the dominant technology, but other chemistries, such as sodium-ion and flow batteries, are showing promise for specific applications. These advancements are pushing the boundaries of what's possible in terms of energy storage capacity and efficiency.
The development of advanced battery chemistries is critical for increasing the overall efficiency and reliability of energy storage systems. The continuous research and development in this area will be crucial to powering the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Beyond Batteries: Alternative Storage Methods
While batteries are prominent, alternative energy storage methods are also gaining traction. Pumped hydro storage, for instance, remains a significant player in large-scale energy storage, benefiting from its proven reliability and high energy storage capacity. Other methods include compressed air energy storage, which leverages the compression and expansion of air to store energy, and thermal energy storage, which stores heat for later use.
These alternative methods often excel in specific applications where battery technology might be less suitable. Factors such as cost, scalability, and environmental impact play a crucial role in determining the optimal storage solution for a given project.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The energy storage market is experiencing substantial growth, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy integration and the rising need for grid stability. Policy support, technological advancements, and decreasing costs are further fueling this expansion. This burgeoning market presents exciting opportunities for innovation and investment in the clean energy sector.
The future of energy storage is bright, promising a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape. The continued development and deployment of advanced technologies will be key to realizing the full potential of this critical sector.
Read more about Decentralization of Energy Generation in Smart Homes
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies