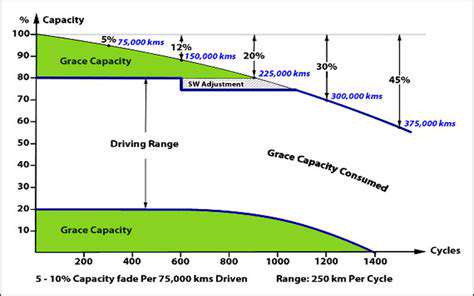
Offshore Wind and Wildlife Protection
Assessing Impacts on Key Marine Species

Assessing the Effects of Pollution on Coral Reefs
Coral reefs are vital marine ecosystems, supporting a vast array of biodiversity and providing crucial ecological services. Pollution from various sources, including agricultural runoff, industrial discharge, and sewage, poses a significant threat to these delicate environments. The chemicals and sediments in polluted runoff can smother coral polyps, hindering their growth and reproduction. This disruption of the delicate balance within the reef ecosystem can lead to the decline of entire coral communities.
Furthermore, the increased nutrient levels in polluted waters can trigger algal blooms, which can outcompete coral for sunlight and nutrients. These blooms, often characterized by large, dense aggregations of algae, can effectively block sunlight from reaching coral, preventing photosynthesis and ultimately leading to coral bleaching and death. The resulting decline in coral populations has cascading effects throughout the marine food web, impacting the survival of fish and other marine life dependent on the reef ecosystem.
Evaluating the Consequences of Overfishing on Fish Populations
Overfishing, a major form of human impact on marine ecosystems, involves harvesting fish at rates exceeding their ability to replenish their populations. This unsustainable practice leads to a drastic reduction in fish stocks, impacting the overall health and productivity of the marine environment. Reduced fish populations can disrupt the natural balance within the food web, having significant consequences for other marine species.
The depletion of specific fish species can have ripple effects throughout the food chain. Predator-prey relationships are disrupted, leading to an imbalance in the ecosystem. The absence of certain fish species can also affect the overall biodiversity of the marine environment, potentially leading to the extinction of other species. This loss of biodiversity undermines the resilience of the ecosystem and makes it more susceptible to further environmental stress.
Analyzing the Impact of Climate Change on Marine Habitats
Climate change is a significant global concern, and its impacts on marine environments are profound and multifaceted. Rising ocean temperatures, driven by increasing greenhouse gas emissions, contribute to coral bleaching events, where corals expel the symbiotic algae that provide them with essential nutrients. This process can lead to widespread coral mortality and the collapse of entire reef ecosystems. The increasing frequency and intensity of these events underscore the urgency of mitigating climate change.
Beyond coral reefs, climate change also affects other marine habitats. Ocean acidification, a consequence of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide absorption by the oceans, threatens the ability of shellfish and other marine organisms to build their calcium carbonate shells and skeletons. This impacts the entire food web, from microscopic plankton to large marine mammals, highlighting the interconnectedness of marine ecosystems.
Examining the Role of Coastal Development in Marine Degradation
Coastal development, driven by human population growth and economic activities, often leads to significant degradation of marine habitats. Construction of ports, harbors, and resorts can directly alter the physical structure of coastal areas, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation. This disruption can negatively affect the diversity and abundance of marine life.
Furthermore, coastal development can introduce pollutants and sediments into the marine environment, potentially harming coral reefs and other sensitive ecosystems. The construction of artificial structures and the alteration of natural coastlines can also disrupt the natural flow of water and sediment, affecting the health and productivity of the marine environment. The impact of these factors on marine ecosystems underscores the importance of careful planning and sustainable development practices.
Mitigation Strategies for Minimizing Impacts

Early Detection and Prevention
Implementing robust early detection mechanisms is crucial for minimizing the impact of potential issues. This involves proactively monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and scrutinizing data streams to identify anomalies or deviations from expected patterns. Early identification allows for swift intervention and mitigates the risk of escalating problems. A well-defined system for reporting and escalating concerns is also essential to ensure timely responses to emerging threats.
Preventive measures, such as security audits and vulnerability assessments, should be conducted regularly. These steps help to identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited. Proactive security measures are a cornerstone of any effective mitigation strategy, significantly reducing the likelihood of incidents. Thorough training programs for personnel on security best practices are also vital components of a comprehensive preventive approach.
Risk Assessment and Analysis
A thorough risk assessment is fundamental to developing effective mitigation strategies. This involves identifying potential threats, evaluating their likelihood and potential impact, and prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their severity. This process should consider both internal and external factors that could negatively affect the system or operation.
A comprehensive risk analysis provides valuable insights into the potential consequences of different scenarios and helps in allocating resources efficiently to address the most critical risks. Understanding the potential impact of various threats is paramount to making informed decisions regarding resource allocation and mitigation efforts. This analysis should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the threat landscape.
Containment and Isolation
In the event of a security breach or other incident, swift containment and isolation procedures are essential to limit the extent of the damage. This may involve isolating affected systems, blocking malicious traffic, and implementing temporary controls to prevent further compromise. Prompt and decisive action in containing the issue can minimize the spread of any negative impact, preventing further escalation and ensuring business continuity.
Effective isolation procedures are critical to preventing further damage and enabling focused remediation efforts. These measures should be clearly defined and practiced regularly to ensure their effectiveness during actual incidents. This includes establishing clear protocols for communication and coordination among stakeholders to facilitate a coordinated response.
Recovery and Remediation
A well-defined recovery plan is crucial for restoring systems and operations to their normal functioning after an incident. This plan should outline the steps needed to identify and fix the root cause of the problem, implement corrective actions, and ensure that similar incidents are prevented in the future. The plan should also include contingency procedures for various scenarios, ensuring business continuity in the event of disruptions.
Remediation efforts should focus on addressing the underlying vulnerabilities that contributed to the incident. This may involve patching software, strengthening security protocols, or implementing new security controls. Thorough documentation of the incident, including lessons learned, is critical for continuous improvement and preventing future occurrences.

Read more about Offshore Wind and Wildlife Protection
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies