Sustainable supply chain and resource optimization
The Imperative for Sustainable Supply Chain Management
The Growing Importance of Sustainability
In today's interconnected world, businesses are increasingly recognizing the critical need for sustainable practices throughout their entire supply chain. Consumers are demanding greater transparency and accountability from companies regarding their environmental and social impact, and investors are increasingly incorporating ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors into their investment decisions. This shift in consumer and investor priorities necessitates a fundamental re-evaluation of traditional supply chain models towards more sustainable alternatives.
Environmental Considerations in Supply Chains
Sustainable supply chains must prioritize minimizing their environmental footprint. This involves reducing carbon emissions throughout the entire lifecycle of products, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing, transportation, and disposal. Implementing eco-friendly packaging, utilizing renewable energy sources, and optimizing transportation routes are crucial steps in achieving this goal. Companies need to assess their current environmental impact and identify areas for improvement.
Social Responsibility and Ethical Sourcing
Beyond environmental concerns, a sustainable supply chain must also uphold social responsibility. This encompasses fair labor practices, ensuring safe working conditions for all employees throughout the chain, and promoting ethical sourcing of raw materials. Transparency and traceability are paramount in ensuring that products are sourced responsibly, avoiding exploitation and promoting fair wages.
Economic Viability and Sustainability
The transition to a sustainable supply chain is not solely about environmental and social responsibility; it's also about economic viability. Efficient resource management, reduced waste, and optimized processes can lead to significant cost savings over the long term. Innovative technologies and solutions can drive efficiency and sustainability, creating a win-win scenario for businesses and the environment.
Technological Advancements and Supply Chain Optimization
Technology plays a pivotal role in achieving sustainability in supply chains. Real-time tracking of goods, predictive analytics for demand forecasting, and blockchain technology for enhanced transparency are just a few examples of how technology can revolutionize supply chain management. These tools enable better resource allocation, reduced waste, and increased efficiency, while simultaneously providing greater visibility and accountability throughout the process.
Collaboration and Partnerships for Change
Sustainable supply chains are not achieved in isolation. Collaboration and partnerships among businesses, suppliers, and stakeholders are essential. Sharing best practices, fostering knowledge exchange, and developing common sustainability goals can accelerate the transition to more sustainable supply chain models. Open communication and collaboration are key to success in this area.
Measuring and Reporting Progress
Implementing a robust system for measuring and reporting progress is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of sustainable supply chain initiatives. Key performance indicators (KPIs) related to environmental impact, social responsibility, and economic viability should be tracked and analyzed regularly. Transparency in reporting allows stakeholders to assess the impact of efforts and provides opportunities for continuous improvement.
Integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Considerations
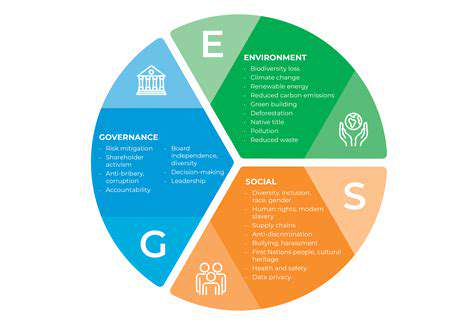
Integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors into Investment Decisions
ESG factors, encompassing environmental, social, and governance considerations, are increasingly gaining traction in the investment world. Investors are recognizing that these factors can significantly influence a company's long-term financial performance and risk profile. By incorporating ESG analysis into their decision-making processes, investors can potentially identify companies with strong sustainability practices and mitigate potential risks associated with environmental damage, social conflicts, or poor corporate governance.
This integration requires a shift in mindset, moving beyond a purely financial focus to one that considers the broader impact of investment decisions. This expanded perspective can lead to more sustainable and responsible investment strategies.
Environmental Considerations in ESG Investing
Environmental factors encompass a wide range of considerations, including climate change, resource depletion, pollution, and biodiversity loss. Investors are increasingly evaluating companies' environmental impact, assessing their carbon footprint, and scrutinizing their resource management practices. Companies with robust environmental policies and innovative solutions in areas like renewable energy or waste management often attract more environmentally conscious investors.
Understanding and assessing a company's environmental footprint is critical in evaluating its long-term viability and potential risks. Companies with a poor environmental record might face regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and potentially decreased profitability.
Social Impact and Stakeholder Engagement
Social factors relate to a company's treatment of its employees, customers, suppliers, and the wider community. These factors include labor practices, human rights, diversity and inclusion, and community relations. Investors are seeking companies that demonstrate strong ethical conduct, fair labor practices, and commitment to community development.
Assessing a company's social impact often involves evaluating its supplier relationships, employee engagement programs, and community involvement initiatives. Evaluating social impact is a complex process, requiring thorough research and a nuanced understanding of the specific industry and context.
Governance Practices and Corporate Responsibility
Governance factors focus on a company's leadership, accountability, and transparency. This includes aspects such as board structure, executive compensation, financial reporting, and anti-corruption measures. Strong corporate governance can foster trust among stakeholders and mitigate risks associated with mismanagement or unethical practices.
Investors often evaluate a company's corporate governance structure to determine its ability to manage risks effectively and ensure long-term sustainability. Poor governance practices can lead to financial instability and reputational damage, negatively impacting a company's value over time.
Data Collection and Analysis for ESG Integration
Accurate and reliable data is crucial for effective ESG integration. This data encompasses environmental performance indicators, social impact assessments, and corporate governance metrics. Accessing and analyzing this data requires sophisticated tools and expertise. A robust data collection process enables investors to identify and analyze potential ESG risks and opportunities.
Developing a standardized and comprehensive data collection framework is essential for effective ESG integration. This framework should be tailored to the specific investment strategy and industry being analyzed.
Challenges and Opportunities in ESG Investing
Integrating ESG factors into investment decisions presents both challenges and opportunities. Data availability and reliability can be problematic in some industries. Investors may also face disagreements over the interpretation and weighting of ESG factors. Despite these challenges, the growing interest in ESG investing provides opportunities for companies to improve their sustainability performance and attract responsible investors.
Further advancements in ESG reporting standards and data accessibility are critical to fostering trust and driving wider adoption of ESG principles in investment decisions.
The Future of ESG Investment Strategies
The future of ESG investment strategies hinges on ongoing innovation and collaboration. The development of advanced analytical tools and standardized reporting frameworks will be crucial. Investors are increasingly seeking more sophisticated and comprehensive ESG assessments. This will lead to a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between ESG factors and financial performance.
Continued research and development in this area will further refine ESG assessment methodologies and enable investors to make more informed and impactful decisions, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
Read more about Sustainable supply chain and resource optimization
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies