From Manual to Mastered: Automating Your Supply Chain
Optimizing Inventory Management Through Data-Driven Automation
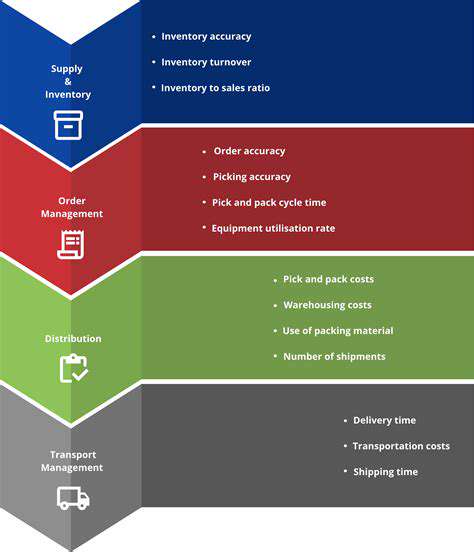
Understanding Inventory Costs
Accurate inventory management hinges on a deep understanding of all associated costs. These costs extend beyond the purchase price of goods, encompassing storage fees, insurance premiums, potential obsolescence, and the opportunity cost of tied-up capital. Understanding these hidden costs is crucial for identifying areas of inefficiency and maximizing profitability. Failing to account for these factors can lead to significant losses in the long run.
Careful analysis of storage space requirements, handling procedures, and potential damage or spoilage rates is essential to minimizing these costs. Proper categorization of inventory items, based on factors such as usage frequency and value, can also play a critical role in optimizing storage strategies and reducing waste.
Implementing Demand Forecasting Techniques
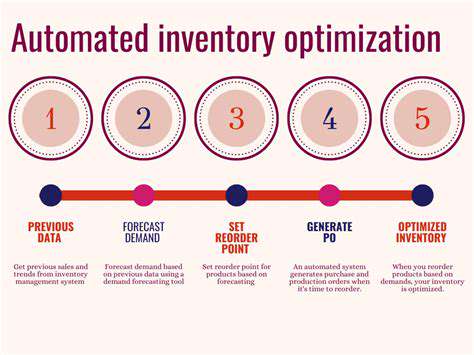
Effective inventory management relies heavily on accurate demand forecasting. This involves analyzing historical sales data, identifying trends, and incorporating external factors like seasonality and market fluctuations to predict future demand. Employing sophisticated forecasting models, such as time series analysis or regression analysis, can significantly improve the accuracy of predictions and minimize inventory discrepancies.
By understanding the patterns in historical sales data, businesses can anticipate future needs and adjust inventory levels accordingly. This proactive approach reduces the risk of stockouts and minimizes the financial burden of carrying excess inventory.
Optimizing Order Placement Strategies
Efficient order placement is paramount for maintaining optimal inventory levels. This involves establishing clear order thresholds, considering lead times, and potentially exploring various order quantities, such as economic order quantities (EOQ). Efficient order placement systems are critical for avoiding stockouts while minimizing storage costs.
Businesses should also evaluate different order fulfillment strategies, such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems, which can further streamline operations and reduce inventory holding costs. Leveraging technology to automate order processing can significantly reduce errors and improve overall efficiency.
Utilizing Inventory Management Software
Inventory management software provides a centralized platform for tracking inventory levels, managing orders, and generating reports. These systems offer a valuable tool for automating tasks, improving data accuracy, and providing real-time insights into inventory performance. This centralized approach is vital for coordinating across different departments and ensuring everyone has access to the latest information.
Using software to manage inventory allows businesses to monitor stock levels in real-time, identify potential shortages or surpluses, and make informed decisions regarding ordering and replenishment. This data-driven approach empowers businesses to optimize their inventory control processes and reduce costs significantly.
Analyzing Inventory Turnover Rate
Analyzing the inventory turnover rate provides valuable insights into the efficiency of inventory management. A high turnover rate indicates that inventory is moving quickly, suggesting efficient sales and minimal holding costs. Conversely, a low turnover rate might signal issues with product demand or pricing strategies.
By understanding the inventory turnover rate, businesses can identify products that are underperforming or overstocked. This information is crucial for making strategic decisions about product assortment, pricing, and marketing efforts.
Implementing Cycle Counting Procedures
Implementing regular cycle counting procedures is essential for maintaining accurate inventory records. This involves periodically counting a portion of the inventory to ensure that the recorded levels match the actual physical quantities. Regular cycle counting allows businesses to identify discrepancies early and prevent larger, more costly errors.
This proactive approach to inventory verification helps avoid costly surprises and ensures that inventory records are reliable. Implementing a consistent cycle counting schedule ensures data accuracy for better decision-making.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Supply Chain Automation Strategies
Optimizing Existing Systems
Moving beyond simply automating individual tasks, advanced supply chain automation strategies focus on optimizing existing systems. This involves integrating disparate automation technologies, such as robotic process automation (RPA) for administrative tasks and warehouse automation systems for material handling, into a unified platform. This holistic approach allows for real-time data flow and analysis, enabling proactive decision-making rather than reactive responses to problems. Such integration ensures data consistency and reduces errors inherent in manually transferring information between different systems. By linking and streamlining processes, companies can achieve greater efficiency and reduce delays across the entire supply chain, leading to significant cost savings.
A key aspect of optimizing existing systems is the implementation of advanced analytics. Leveraging data from various sources within the supply chain, including inventory levels, demand forecasts, and transportation data, allows for predictive modeling. This predictive capability enables companies to anticipate potential disruptions and adjust their operations accordingly, minimizing the impact of unforeseen circumstances. Predictive analytics can identify bottlenecks, predict demand fluctuations, and optimize resource allocation, resulting in a more resilient and adaptable supply chain.
Embracing Emerging Technologies
The future of supply chain automation lies in embracing emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, enabling proactive risk management and improved decision-making. This goes beyond basic forecasting; AI can predict potential supply chain disruptions, such as unexpected weather events or geopolitical instability, allowing companies to proactively adjust their strategies and mitigate risks. The ability for AI to adapt to changing circumstances is a crucial advantage in today's dynamic business environment.
Machine learning algorithms can further enhance these capabilities by continuously learning and improving their predictive models over time. This iterative learning process allows for increasingly accurate forecasting and optimization of resource allocation, leading to more efficient and cost-effective supply chain operations. As these technologies mature, their integration into supply chain management will become increasingly essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Another key emerging technology is the Internet of Things (IoT). By connecting various devices and equipment throughout the supply chain, real-time visibility into inventory, transportation, and production is significantly enhanced. This level of transparency allows for faster identification of problems, quicker response times, and more effective resource management. Real-time tracking and monitoring of goods in transit, for example, can provide valuable insights into potential delays and allow for proactive intervention to ensure timely delivery.
The integration of blockchain technology can further enhance transparency and security within the supply chain. By creating a secure and immutable record of transactions, blockchain can help track products from origin to destination, ensuring authenticity and traceability. This level of visibility and accountability is critical for building trust with customers and partners, particularly in industries with stringent regulatory requirements.
Implementing these technologies requires careful planning and a phased approach. Companies must consider the specific needs of their supply chain and choose the technologies that best align with their goals and resources. A thorough assessment of existing systems and processes is essential to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of these emerging technologies.
Furthermore, companies need to invest in training and development programs to equip their employees with the necessary skills to effectively utilize these advanced technologies.
Read more about From Manual to Mastered: Automating Your Supply Chain
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies