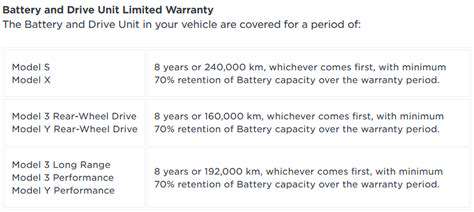
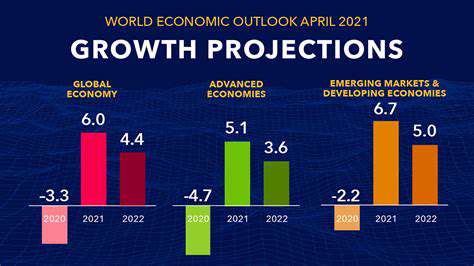
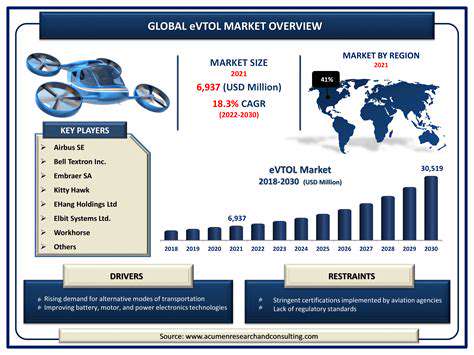
The Importance of Data Privacy Regulations for EVs
Data minimization is a fundamental principle in data protection that emphasizes collecting and processing only the minimum amount of personal data necessary to achieve a specific, legitimate purpose. This principle is crucial for ensuring that individuals' privacy is respected and that their data is not unnecessarily exposed to potential risks. By limiting the scope of data collection, organizations reduce the potential for misuse, accidental disclosure, or breaches, ultimately enhancing the overall security and trustworthiness of their data handling practices. Organizations should carefully evaluate the specific data points required for each process, and only collect those directly relevant to the defined purpose. In essence, data minimization is about avoiding the collection of extraneous data that could potentially lead to privacy violations or security vulnerabilities.
A practical application of data minimization involves carefully considering the specific needs of each process. For example, if a company needs to process customer data for order fulfillment, it should only collect the data directly relevant to that purpose, such as name, address, and order details. Avoid collecting unnecessary data like detailed medical history or financial information, unless it's explicitly required for the specific purpose and legally permissible. This approach not only safeguards individual privacy but also simplifies data management, reduces storage costs, and minimizes the risk of errors or inconsistencies. Ultimately, data minimization is a proactive measure that promotes responsible data handling practices and fosters trust with data subjects.
Purpose Limitation: Ensuring Data is Used Only for Intended Purposes
Purpose limitation is a critical aspect of data protection that mandates that personal data should only be processed for the specific, explicit, and legitimate purposes for which it was collected. This principle underscores the importance of transparency and accountability in data handling. It prevents the use of data for purposes beyond those initially agreed upon, thereby preserving the individual's right to privacy and control over their personal information. Failure to adhere to purpose limitation can lead to a breach of trust and potentially serious legal consequences.
A crucial example of purpose limitation involves a company collecting customer data for marketing purposes. They should not use that same data for unrelated activities like targeted advertising campaigns without explicit consent from the customer. Clear and concise communication of data usage policies and obtaining explicit consent for secondary uses are essential components of purpose limitation. This approach not only respects individual autonomy but also builds trust by demonstrating a commitment to ethical data handling. By adhering to purpose limitation, organizations maintain the integrity and security of personal data, ensuring its use aligns with the legitimate reasons for collection.
Addressing Data Security and Breach Prevention
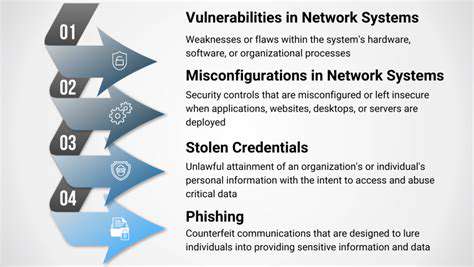
Understanding Data Breaches
Data breaches are a significant concern in today's digital age, impacting individuals and organizations alike. Understanding the various types of data breaches, from simple phishing scams to sophisticated hacking attacks, is crucial for developing effective security measures. Data breaches can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage. Protecting sensitive information is paramount in mitigating the risks associated with these breaches.
These incidents often involve unauthorized access to confidential data, leading to the exposure of personal information, financial records, and intellectual property. The consequences can be devastating, ranging from identity theft to severe financial repercussions. Recognizing the potential vulnerabilities within systems and networks is the first step towards implementing robust security protocols.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Implementing robust security measures is vital for protecting sensitive data. This includes implementing strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating software and security protocols. Organizations should prioritize employee training on cybersecurity best practices to minimize the risk of phishing attacks and social engineering tactics. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are also essential components for proactive risk management.
Security awareness training for employees is critical, teaching them how to identify and avoid phishing attempts. Strong passwords, combined with multi-factor authentication, are fundamental for securing accounts and systems. Regular software updates and patches are essential to address known vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information. Encrypting data both in transit and at rest is a critical step in preventing unauthorized access. Implementing strict access controls, limiting access to only authorized personnel, is also essential. This involves defining clear roles and responsibilities for handling sensitive data. Strong access control measures, including role-based access control (RBAC), are key to reducing the attack surface.
Incident Response Planning
Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for mitigating the impact of a potential data breach. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, including notification procedures, containment strategies, and recovery plans. A proactive approach to incident response is essential, minimizing the damage and disruption caused by a security breach. Regularly testing and updating this plan is vital to ensure its effectiveness.
Developing a comprehensive incident response plan is critical for effectively handling security breaches. This plan should encompass procedures for containing the breach, notifying affected parties, and restoring systems to normal operation. Regular reviews and updates are crucial to ensure the plan remains relevant and effective in a rapidly evolving threat landscape. This proactive approach helps limit the damage and disruption caused by a security incident.
Data Security Awareness
Promoting data security awareness among employees and stakeholders is fundamental. Regular training sessions and awareness campaigns are crucial for enhancing security practices. Educating users about common threats and best practices is essential for creating a security-conscious culture. This includes explaining the importance of strong passwords, safe internet practices, and the risks associated with phishing attacks. Cultivating a culture of security awareness throughout the organization is crucial for effective data protection.
Raising awareness about data security best practices is paramount. This involves providing ongoing training and resources to employees, encouraging them to report suspicious activity, and promoting a culture of security vigilance. Empowering employees to become active participants in safeguarding sensitive data is essential for a robust and resilient security posture.