Analyzing Life Cycle Emissions of EVs and ICE Vehicles
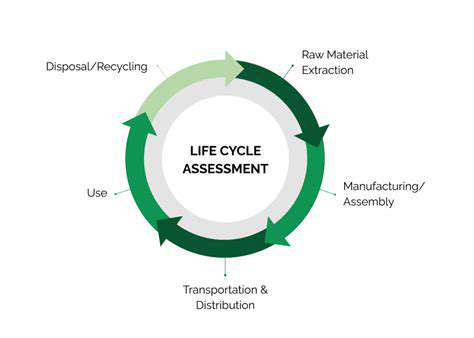
Raw Material Extraction and Manufacturing Processes
Raw Material Acquisition
The initial stage of any manufacturing process involves the acquisition of raw materials. This encompasses everything from sourcing the necessary minerals, ores, or agricultural products to the transportation and initial processing steps. The environmental impact of this stage can be significant, ranging from deforestation and habitat destruction to the energy consumption associated with mining and transportation. Understanding the specific processes and their associated emissions is crucial for accurately assessing the overall life cycle impact of a product.
Careful selection of suppliers and adherence to sustainable sourcing practices are essential to minimizing environmental harm during this crucial phase. Transparency in supply chains is also key to identifying and mitigating potential negative impacts throughout the entire process, from the initial extraction to the final product.
Mineral Processing and Refining
Many raw materials require extensive processing and refining before they can be used in manufacturing. This often involves energy-intensive techniques like crushing, grinding, and chemical treatments. The emissions generated during these processes, including greenhouse gases, particulate matter, and potentially hazardous substances, need to be thoroughly evaluated. Furthermore, the specific energy sources utilized in these refining operations significantly influence the overall carbon footprint.
Extraction of Metals and Minerals
The extraction of metals and minerals from the earth, whether through mining or quarrying, often involves significant environmental disruption. The extraction process can lead to soil erosion, water contamination, habitat destruction, and the release of harmful substances into the surrounding environment. Careful consideration of these factors is necessary to minimize the negative environmental consequences associated with these activities.
Understanding the specific geological conditions and the types of extraction methods employed is critical for accurately assessing the environmental impact of this phase. Effective mitigation strategies, such as the implementation of reclamation practices, are essential to minimize long-term environmental damage.
Manufacturing Processes and Energy Consumption
The manufacturing process itself consumes substantial amounts of energy, often relying on fossil fuels for power. The type and amount of energy used directly impacts the overall emissions profile. Energy-efficient technologies and alternative energy sources can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of this stage. Analyzing the specific energy sources utilized in the manufacturing process is crucial for understanding the environmental impact of the product.
Chemical Conversion and Processing
Many manufacturing processes involve chemical conversions and complex treatments of raw materials. These steps often release various chemical substances into the air, water, and soil. Understanding the specific chemical reactions and the associated emissions is vital for a comprehensive assessment of the life cycle impact. Implementing cleaner production techniques and using less hazardous chemicals are necessary steps to minimize the environmental impact of these procedures. This also requires precise monitoring of emissions and waste management.
Waste Management and Disposal
The generation of waste is an inevitable part of the manufacturing process. Managing this waste effectively, including recycling and proper disposal methods, is critical to reducing the overall environmental impact. The disposal and recycling methods chosen significantly affect the environmental consequences. Careful consideration of waste management strategies during the manufacturing process is crucial for minimizing the environmental burden of the product throughout its entire life cycle.
Transportation and Logistics
The transportation of raw materials and finished goods plays a significant role in the overall life cycle emissions. The distance of transportation, the mode of transport (e.g., truck, ship, rail), and the efficiency of the logistics network all influence the carbon footprint. Optimizing transportation routes, utilizing more fuel-efficient vehicles, and exploring alternative transportation methods can substantially reduce the environmental impact of this stage. The environmental impacts of transportation must be thoroughly evaluated and mitigated through effective logistical planning.
Read more about Analyzing Life Cycle Emissions of EVs and ICE Vehicles
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies