Decentralized Energy for Energy Access in Developing Countries: Impact and Scale

Decentralized Systems and Community Ownership
Decentralized renewable energy systems, often situated at the community level, offer a significant advantage over centralized grids. This approach fosters greater local control and ownership, empowering communities to manage and benefit directly from their energy production. This localized control is crucial in areas with unreliable grid access or where grid infrastructure is underdeveloped, allowing communities to maintain a reliable energy supply, even during outages. Moreover, decentralized systems can be more resilient to natural disasters and other disruptions, as damage to one system does not necessarily cripple the entire network.
Distributed generation, a cornerstone of decentralized systems, brings renewable energy sources closer to the point of consumption. This proximity reduces transmission losses, potentially saving energy and lowering costs. Furthermore, community-owned renewable energy projects can foster a sense of collective responsibility and participation, creating a more sustainable and equitable energy future. Community engagement and ownership are crucial for long-term success.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Beyond the immediate benefits of energy independence, decentralized renewable energy projects can stimulate local economies. Job creation in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of these systems can revitalize local industries, leading to increased employment opportunities and income generation for community members. Investing in these local economies strengthens the overall community and reduces reliance on external energy providers.
The environmental benefits are equally compelling. Decentralized systems, by their nature, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, resulting in significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. This transition to cleaner energy sources directly combats climate change and protects public health, contributing to a more sustainable environment for future generations. Furthermore, the use of renewable resources, like solar and wind, reduces our dependence on finite resources, ensuring a more secure and stable energy supply for years to come.
Reduced transmission losses, enhanced energy security, and the potential for local economic growth all contribute to the compelling case for decentralized renewable energy. These systems offer a pathway to a more resilient, sustainable, and equitable energy future for communities worldwide.
Community engagement and ownership are paramount for the successful implementation of decentralized renewable energy projects. This active participation ensures that these projects meet the specific needs and priorities of the local community, fostering long-term sustainability.
The reduction in reliance on centralized grids and fossil fuels translates directly into a decrease in our environmental impact. This approach is crucial for mitigating climate change and preserving the health of our planet.
The Impact of Decentralized Energy on Local Communities
Decentralized Energy: A Shift in Power Dynamics
Decentralized energy systems represent a fundamental shift in the traditional power paradigm, moving away from centralized, large-scale generation towards smaller, localized sources. This shift has profound implications for local communities, empowering them with greater control over their energy resources and potentially reducing their reliance on distant, often unreliable, power grids. This distributed approach fosters a sense of community ownership and responsibility, encouraging active participation in energy production and management.
Economic Opportunities for Local Businesses
The rise of decentralized energy sources creates new economic opportunities for local businesses. From installing and maintaining solar panels to providing energy storage solutions, a burgeoning industry emerges, creating jobs and fostering entrepreneurship within the community. Furthermore, the potential for local energy production can reduce reliance on imported fuels, boosting local economies and creating more resilient business models.
Enhanced Community Resilience in the Face of Disasters
Decentralized energy systems offer a significant advantage in disaster preparedness and response. Local, distributed energy sources are less susceptible to widespread outages caused by natural disasters or grid failures. This resilience ensures a continued supply of energy during critical periods, enabling essential services and community support to function even in the face of adversity. This enhanced resilience is particularly valuable in remote or vulnerable areas.
Improved Energy Access for Underserved Communities
Decentralized energy solutions can play a crucial role in bridging the energy access gap, particularly in underserved communities. Small-scale renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, can be deployed in areas lacking access to traditional grid infrastructure, bringing electricity and other essential services to previously marginalized populations. This access can dramatically improve quality of life and support economic development.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
The shift towards decentralized energy systems has significant environmental benefits. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, communities can decrease greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Renewable energy sources, integral to decentralized systems, promote a cleaner and more sustainable approach to energy production, improving air quality and fostering a healthier environment for future generations. This sustainable model also reduces the environmental footprint of energy consumption.
Addressing Grid Reliability Concerns
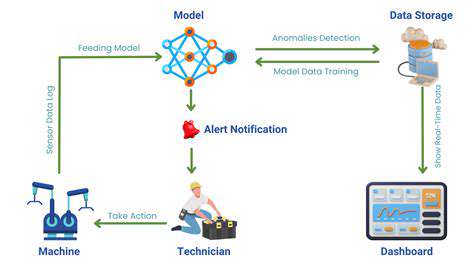
One of the primary concerns surrounding decentralized energy is the potential impact on grid reliability. However, smart grid technologies and advanced energy storage solutions are addressing these concerns. These innovations can integrate decentralized energy sources smoothly into the existing grid, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply while harnessing the benefits of distributed generation. The combination of these technologies can create a more robust and resilient energy infrastructure.
Citizen Engagement and Community Empowerment
Decentralized energy systems foster greater citizen engagement and community empowerment. Local residents can become active participants in the energy production and distribution process, promoting a sense of ownership and responsibility. This increased participation can lead to more sustainable energy practices and a stronger sense of community cohesion. The direct involvement empowers residents and strengthens community ties.
Future Outlook and the Role of Technology

Technological Advancements Shaping the Future
The rapid pace of technological advancement is undeniably reshaping the world around us, impacting every facet of human life. From artificial intelligence and machine learning to advancements in biotechnology and nanotechnology, the future holds immense potential for progress and innovation. These advancements are not just theoretical concepts; they are already transforming industries, creating new jobs, and addressing some of humanity's most pressing challenges.
We are witnessing the emergence of smart cities, personalized medicine, and sustainable energy solutions, all powered by cutting-edge technologies. These developments promise to significantly improve quality of life, enhance efficiency, and solve global problems like climate change and resource scarcity. The integration of technology into our daily lives is accelerating at an unprecedented rate, and its impact on future generations will be profound and far-reaching.
The Impact of Technology on the Workforce
The integration of technology into the workplace is fundamentally altering the nature of work itself. Automation and AI are poised to automate many routine tasks, potentially displacing some workers in certain sectors. However, this transformation also presents opportunities for new job creation in emerging fields like data science, AI development, and robotics engineering. Adapting to this evolving landscape requires continuous upskilling and reskilling initiatives to ensure that the workforce remains competitive and productive.
The future workforce will need to embrace new skills and knowledge. Learning to collaborate effectively with AI systems, understanding data analysis and interpretation, and possessing strong problem-solving abilities will be crucial for success in the coming years. Employers will need to invest in training and development programs to equip their employees with the skills needed to thrive in this rapidly changing technological environment.
The Ethical Considerations and Societal Implications
As technology continues to advance, it's crucial to address the ethical considerations and societal implications that accompany it. Issues like data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for misuse of advanced technologies require careful attention and responsible development. Establishing clear ethical guidelines and regulations is essential to ensure that technological progress benefits all members of society and does not exacerbate existing inequalities.
The societal impact of these advancements is multifaceted. We need to consider how technology impacts social interactions, communication patterns, and the very fabric of our communities. Discussions surrounding the ethical implications of artificial intelligence, genetic engineering, and other emerging technologies will be critical in shaping a future that is both innovative and equitable.
The integration of technology into education, healthcare, and other critical sectors must be approached with caution. Careful consideration must be given to the potential for unintended consequences and the need to mitigate any negative impacts on vulnerable populations. The development of robust regulatory frameworks, coupled with ongoing public dialogue, will be essential in navigating these complex ethical challenges.
Read more about Decentralized Energy for Energy Access in Developing Countries: Impact and Scale
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies