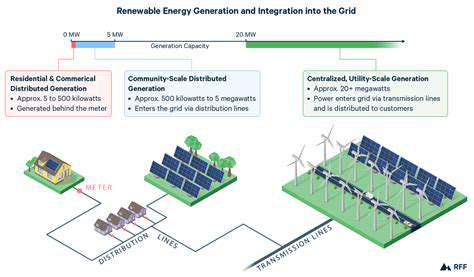
Renewable Energy and Green Hydrogen: A Powerful Duo
Understanding Green Hydrogen
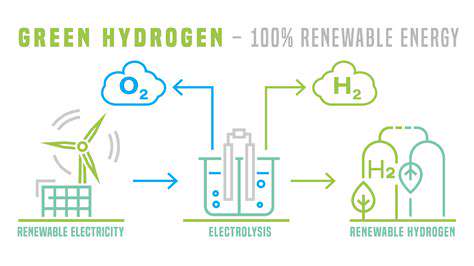
Green hydrogen, a clean energy carrier, is produced through the electrolysis of water using renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. This process splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, with no harmful emissions. Unlike traditional methods of hydrogen production, which often rely on fossil fuels, green hydrogen offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative. This crucial difference sets the stage for its potential to revolutionize various sectors, from transportation to energy storage.
The fundamental principle behind green hydrogen production is its reliance on renewable energy. This makes it a key component in the transition towards a sustainable energy future. The process of electrolysis itself is relatively straightforward, though the efficiency and scalability of the technology are still areas of ongoing research and development.
Production Methods and Technologies
Electrolysis, the primary method for producing green hydrogen, involves using an electric current to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Various electrolysis technologies are being developed, including alkaline, proton exchange membrane (PEM), and solid oxide electrolysis. Each technology has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, cost, and scalability. The choice of technology often depends on factors such as the specific renewable energy source available and the desired application of the hydrogen.
The efficiency of these electrolysis processes is constantly improving, leading to lower costs and greater feasibility for widespread adoption. Researchers are exploring ways to optimize the processes and reduce the energy consumption required for hydrogen production, paving the way for even more widespread implementation.
Applications in Various Sectors
Green hydrogen is not limited to a single application; its versatility makes it a potential game-changer across multiple sectors. In transportation, it can power fuel cells in vehicles, offering a zero-emission alternative to gasoline and diesel. Furthermore, green hydrogen can be used in industrial processes, replacing fossil fuels in sectors such as steel production and ammonia synthesis.
Beyond transportation and industry, green hydrogen can play a vital role in energy storage. It can be stored and transported, allowing for the management of fluctuating renewable energy sources like solar and wind, ensuring a consistent and reliable energy supply. This adaptability is a key factor in its potential for widespread adoption.
Economic Viability and Cost Considerations
The economic viability of green hydrogen production is a crucial aspect of its widespread adoption. While the initial costs of establishing green hydrogen production facilities can be substantial, the long-term benefits, including reduced reliance on fossil fuels and the creation of new jobs, can make it a worthwhile investment. Government policies and incentives can play a significant role in accelerating the development and deployment of green hydrogen technologies, leading to a more competitive market.
The cost of green hydrogen is expected to decrease as technology improves and production scales up. Increased competition among producers and advancements in electrolysis techniques will contribute to making green hydrogen more affordable and accessible to various sectors.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
The environmental advantages of green hydrogen are undeniable. By replacing fossil fuels with green hydrogen, we drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment. This shift towards sustainable energy sources is critical for mitigating climate change and protecting future generations.
Green hydrogen's production process relies on renewable energy sources, making it a truly sustainable energy carrier. This inherent sustainability is a key factor in its appeal for a wide range of applications, as it aligns perfectly with the growing global commitment to environmentally friendly solutions.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its numerous benefits, green hydrogen faces challenges, including the need for improved storage and transportation infrastructure. Developing efficient and cost-effective methods for storing and transporting hydrogen is crucial for its widespread adoption. Furthermore, scaling up production to meet future demand requires significant investment and technological advancements.
The future outlook for green hydrogen is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving efficiency and reducing costs. Government support, coupled with continued innovation, will be key to unlocking the full potential of green hydrogen and its role in a sustainable future.
Pinpointing repetitive motions is crucial in understanding potential hand pain triggers. Consider your daily tasks, both at work and at home. Do you frequently perform actions like typing, gripping tools, or using a mouse for extended periods? These seemingly mundane activities, when repeated excessively, can strain the small muscles and tendons in your hands, leading to inflammation and pain. Analyzing the frequency and duration of these motions is a key step in assessing your current setup.

Challenges and Future Outlook

Navigating the Complexities of the Current Landscape
The current technological landscape is characterized by rapid advancements and evolving consumer expectations, creating both exciting opportunities and significant challenges for businesses. Adapting to these changes requires a proactive approach to innovation and a deep understanding of emerging trends. Staying ahead of the curve in this dynamic environment demands continuous learning and a willingness to embrace new technologies, while simultaneously managing potential risks and ensuring a smooth transition for existing operations. This includes not only technological advancements but also shifts in consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Furthermore, the increasing interconnectedness of systems and data presents both opportunities for efficiency and potential vulnerabilities. Businesses must prioritize robust cybersecurity measures and develop strategies for data protection and privacy. A proactive approach to risk management is crucial for mitigating potential threats and safeguarding valuable assets. This includes not only technical solutions but also well-defined policies and procedures for data handling and security.
Forecasting Future Trends and Preparing for Change
Anticipating future trends and preparing for potential disruptions is essential for long-term success. Market research, analysis of emerging technologies, and engagement with industry experts can provide valuable insights into the direction of the market and the likely challenges that lie ahead. This forward-thinking approach allows businesses to develop strategies that are both adaptable and resilient in the face of change.
Understanding the evolving needs and expectations of consumers is critical. This includes staying abreast of the latest trends in communication, commerce, and social interaction. A deep understanding of customer preferences and market demands is essential for developing products and services that meet these evolving needs. This ongoing engagement with consumers will position businesses for success in the future.
Ensuring Sustainable and Responsible Growth
Sustainable and responsible growth is no longer a niche consideration but a core requirement for success in today's world. Businesses must carefully consider the environmental and social impact of their operations. This includes adopting environmentally friendly practices, promoting ethical labor standards, and supporting initiatives that contribute to a more sustainable future. Companies that prioritize these aspects will not only enhance their reputation but also build a strong foundation for long-term success.
Integrating social responsibility into core business strategies is paramount. This encompasses not only ethical sourcing and production but also community engagement and philanthropic initiatives. By incorporating social responsibility principles, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to a more equitable and sustainable future, building loyalty and trust with stakeholders.
Read more about Renewable Energy and Green Hydrogen: A Powerful Duo
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies