The Impact of Distributed Energy Systems on EV Growth
Improving Grid Stability and Enhancing Sustainability
Improving Grid Stability
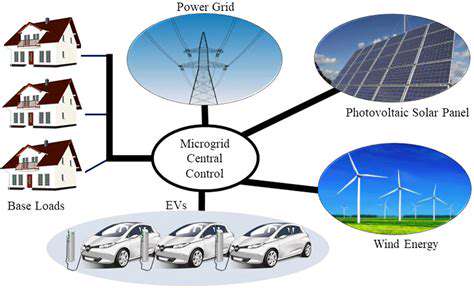
Grid stability is crucial for reliable and efficient energy delivery. Distributed energy resources (DERs), such as rooftop solar panels and battery storage systems, can introduce variability and volatility into the grid's operation. This variability necessitates sophisticated control mechanisms and advanced grid management strategies to maintain frequency and voltage within acceptable limits. Effective communication and coordination between DERs and the grid are essential to ensure smooth integration and prevent instability, especially during periods of high solar irradiance or low load.
Implementing smart grid technologies, including advanced sensors, communication networks, and control systems, is vital for monitoring and managing grid conditions in real-time. These technologies allow for proactive responses to emerging instability issues, enabling grid operators to dispatch resources and adjust grid parameters dynamically to maintain stability and prevent cascading failures. This approach can significantly enhance the resilience of the grid against unforeseen events.
Enhancing Sustainability Through DER Integration
The integration of distributed energy resources (DERs) is a key component in achieving greater sustainability in the energy sector. By decentralizing energy production, DERs reduce reliance on large, centralized power plants, thereby lowering transmission losses and greenhouse gas emissions. This shift towards distributed generation also fosters energy independence for communities and reduces reliance on long-distance energy transmission infrastructure, which can be expensive and environmentally impactful.
Furthermore, DERs can improve the efficiency of energy use. Smart grid technologies enable better matching of energy generation with demand, reducing energy waste and optimizing energy consumption patterns. This optimization process can significantly contribute to a more sustainable energy system overall. Incorporating renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the distributed energy generation portfolio further enhances sustainability goals.
Economic Benefits of Distributed Generation
The integration of distributed energy resources (DERs) presents significant economic advantages. By reducing reliance on expensive centralized power plants, DERs can lead to lower energy costs for consumers and businesses. The reduced need for grid upgrades and maintenance can also translate into substantial savings for utilities. Moreover, the creation of local energy markets can foster local job creation and economic development. Incentives and policies that support DER deployment can further stimulate economic growth.
Grid Management and Control Systems
Advanced grid management and control systems are crucial for effectively integrating distributed energy resources (DERs) into the grid. These systems must be able to handle the fluctuating nature of DER output and coordinate the operation of various distributed energy resources. Real-time monitoring and control are essential to ensure grid stability and prevent potential disruptions. The development of robust communication protocols and data management systems are vital for enabling seamless integration and optimal control of DERs.
Addressing Intermittency Challenges
The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, poses challenges for grid stability. Distributed energy resources (DERs) often rely on these intermittent sources, necessitating the development of sophisticated energy storage solutions and demand-response programs. Effective energy storage systems, such as batteries and pumped hydro, can help to smooth out the fluctuations in renewable energy generation and ensure consistent grid supply. Developing smart demand-response programs that incentivize consumers to adjust their energy consumption based on real-time grid conditions is also crucial.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Appropriate policy and regulatory frameworks are essential for facilitating the successful integration of distributed energy resources (DERs) into the grid. Clear guidelines and incentives are needed to encourage investment in DER technologies and support their deployment. Regulations should address issues such as grid interconnection standards, net metering policies, and the management of distributed energy resources. Support for research and development in DER technologies and grid management solutions is also vital for fostering innovation and ensuring a smooth transition to a more sustainable and reliable energy system. Policies should promote the adoption of DERs while ensuring grid stability and reliability.
Read more about The Impact of Distributed Energy Systems on EV Growth
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies