Comparing EV Charging Network Expansion Strategies
The global landscape of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure is rapidly evolving, with significant disparities across regions. While some developed nations boast extensive networks of public charging stations, many developing countries are still in the early stages of establishing such infrastructure. This disparity in access highlights the need for international collaboration and targeted investment to ensure equitable access to charging for all EV owners.
Different countries and regions have adopted varying approaches to EV charging infrastructure development. Some prioritize fast-charging stations for long-distance travel, while others focus on slower, home-based charging options. These differing strategies reflect varying needs and priorities, emphasizing the need for flexible and adaptable charging solutions.
Public vs. Private Charging Stations
Public charging stations are crucial for long-distance travel and offer convenience for drivers on the go. These stations often come in various types, from slow AC charging to high-powered DC fast charging, catering to different needs and vehicle types. The availability and accessibility of public charging stations are often a key determinant in the adoption and widespread use of EVs.
Conversely, private charging solutions, such as home charging stations, offer convenience and cost-effectiveness for daily commutes and parking spaces. These solutions are often tailored to the individual's needs and typically require less public investment. However, they may face limitations in terms of accessibility to some segments of the population, necessitating a balanced approach to address both public and private charging needs.
Charging Station Technology and Standards
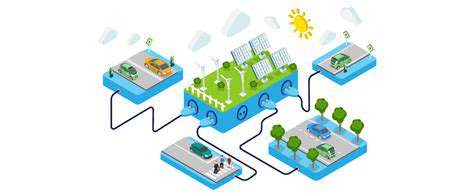
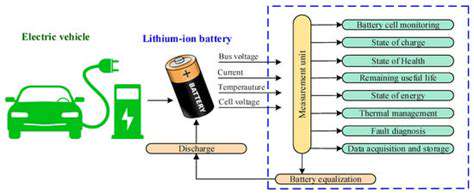
The technology behind EV charging stations is constantly evolving, with advancements in charging speeds, efficiency, and safety protocols. The integration of smart charging technologies is particularly important for optimizing energy grids and managing peak demand. This integration plays a crucial role in the broader goal of creating a sustainable and efficient energy system.
Different countries and regions have adopted varying charging standards, which can present challenges for EV drivers traveling internationally. Harmonizing standards is critical to ensure seamless charging experiences and facilitate the widespread adoption of EVs across borders and continents. This requires international collaboration and standardization efforts to overcome these obstacles.
The Role of Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a significant role in shaping the development and adoption of EV charging infrastructure. Subsidies for EV purchases, tax credits, and regulations promoting the installation of charging stations are examples of such initiatives. These incentives can significantly influence consumer behavior and encourage wider adoption.
Governments also need to consider the broader implications of EV charging infrastructure development, such as grid modernization and the potential environmental impact of manufacturing and installing charging stations. A comprehensive approach that considers these factors is essential to ensure a sustainable and equitable transition to EVs.
Future Trends in EV Charging
The future of EV charging is likely to be characterized by increased charging speeds, greater accessibility, and more seamless user experiences. Smart charging technologies will become more prevalent, optimizing energy usage and grid management. The integration of renewable energy sources into charging stations will also be crucial for a sustainable future.
Further advancements in battery technology, combined with the continuing development of charging infrastructure, are expected to drive further innovation and adoption of electric vehicles globally. This will require a continuous effort to overcome challenges and to ensure that the charging experience is safe, reliable, and accessible to all.