Exploring Future EV Export Policies and Trade Norms
Export Regulations and the Global EV Market
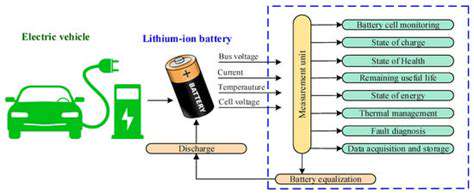
As the electric vehicle (EV) industry expands, navigating export regulations has become a critical challenge for businesses. The landscape is shaped by a mix of international trade agreements, national policies, and environmental considerations. Companies must stay agile to adapt to these shifting frameworks, which present both roadblocks and openings for growth. Market access often hinges on understanding regional compliance requirements.
While consumer demand for EVs surges globally, regulatory misalignment between markets creates friction. For instance, battery certification standards in Europe may differ sharply from Asian or North American requirements. This disparity forces exporters to maintain multiple production configurations.
Impact of Trade Agreements on EV Exports
Modern trade pacts increasingly include EV-specific clauses covering everything from tariff reductions to technology transfer rules. The USMCA's automotive rules of origin, for example, mandate specific regional value content for qualifying vehicles. Such provisions can dramatically alter cost structures, making some export routes suddenly viable while rendering others uneconomical.
However, these agreements often come with strings attached. The EU's recent trade deals require exporters to demonstrate ethical mineral sourcing and carbon-neutral production methods. These conditions, while laudable, add layers of documentation and verification processes.
Environmental Regulations and EV Exports
Global emissions targets are reshaping EV design requirements. The EU's proposed Battery Passport system would track each battery's carbon footprint from mine to showroom. Similar initiatives are emerging in California and China. Forward-thinking manufacturers are preemptively adopting lifecycle analysis tools to future-proof their compliance strategies.
Beyond emissions, regulations now target specific components. Norway's proposed ban on certain flame retardants in EV interiors could force material substitutions across export models. Such localized requirements complicate global product standardization efforts.
Battery Material Sourcing and Supply Chains
The geopolitical dimension of battery minerals cannot be overstated. Indonesia's nickel export restrictions and Chile's lithium nationalization talks demonstrate how quickly material flows can be disrupted. Smart manufacturers are diversifying supplier networks while investing in battery recycling infrastructure as a hedge against raw material volatility.
New trade corridors are emerging in response. The recent US-Japan critical minerals agreement bypasses traditional supply routes, illustrating how policy can reshape logistics networks overnight. Exporters must monitor these developments closely.
Safety Regulations and Standards for EV Exports
Safety protocols are converging around UNECE standards, but regional exceptions persist. China's GB/T charging interface standard creates compatibility hurdles for foreign EVs, while US crash test requirements differ from Euro NCAP protocols. These variations force costly adaptations for global market entrants.
Labor Standards and EV Production
The ethical spotlight on EV supply chains intensifies yearly. Recent legislation like the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act imposes strict accountability for overseas labor practices. Exporters must now audit multiple tiers of suppliers, from cobalt mines to component factories, to avoid regulatory penalties and consumer backlash.
This scrutiny extends to carbon accounting. France's upcoming border carbon adjustments will penalize imports based on production emissions, making cleaner manufacturing a competitive advantage.
Intellectual Property Rights and EV Exports
As EV technology proliferates, IP protection becomes paramount. Battery chemistry patents and charging system designs represent billions in R&D investment. Manufacturers exporting to markets with weak IP enforcement risk losing control of their innovations through forced technology transfers or reverse engineering.
The rise of open patent pools in some regions adds complexity, requiring careful navigation of shared vs. proprietary technology boundaries.
Addressing Challenges and Opportunities in EV Export Logistics

Identifying Key Challenges
The EV export ecosystem presents unique hurdles. Battery transport regulations classify lithium-ion packs as dangerous goods, requiring specialized handling. Ocean freight costs have become unpredictable, while some ports lack charging infrastructure for vehicle processing. These operational pain points can erase thin export margins if not managed proactively.
Customs clearance times vary wildly by market. Some nations lack harmonized EV classification systems, causing delays. A single missing certificate for battery components can strand entire shipments.
Exploring Opportunity Areas
Creative solutions are emerging. Some exporters now use blockchain for real-time customs documentation, while others establish regional assembly hubs to circumvent import barriers. The growth of AI-powered logistics platforms helps optimize routes based on regulatory constraints and infrastructure availability.
Secondary markets for refurbished EVs are blossoming in Southeast Asia and Africa, creating new export channels for older models that no longer meet strict EU or US standards.
Developing Strategic Solutions
Leading firms adopt modular designs that simplify regional adaptation. A swappable charging port module, for instance, allows quick reconfiguration for different markets. This approach reduces the need for separate production lines while maintaining compliance flexibility.
Joint ventures with local distributors can navigate regulatory mazes more effectively than going solo. A partner familiar with domestic certification processes can shave months off market entry timelines.
Implementing and Monitoring Progress
Effective export operations now require dedicated regulatory tracking teams. These units monitor policy changes globally, using automated alerts for relevant updates. Monthly compliance audits ensure no new requirement slips through the cracks.
Adapting to Change and Future Trends
The coming wave of solid-state batteries and sodium-ion technology will rewrite export playbooks. Forward-looking firms are already engaging standards bodies to shape the next generation of export regulations rather than just reacting to them.
Trade agreement negotiations increasingly include EV industry representatives, recognizing that export rules can make or break national electrification goals. Active participation in these discussions ensures practical considerations aren't overlooked.
Read more about Exploring Future EV Export Policies and Trade Norms
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies