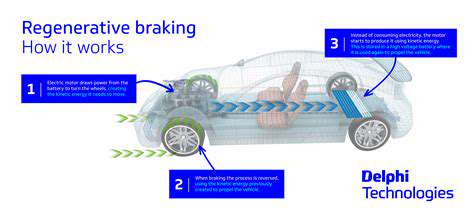
How EVs Are Revolutionizing Last Mile Delivery
Adapting to the Infrastructure and Charging Needs
Infrastructure Considerations for EV Adoption
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) hinges critically on the availability of robust and accessible charging infrastructure. Simply put, if drivers can't easily and conveniently recharge their vehicles, the transition to EVs will be significantly hampered. This necessitates a multifaceted approach, ranging from strategically placed public charging stations to the development of home charging solutions. Significant investment in upgrading existing power grids to handle the increased demand for electricity from EVs is also paramount for long-term sustainability and reliability.
The geographical distribution of charging stations is also a key factor. Current models need to consider not just urban areas, but also rural communities and highways. A lack of charging options in these areas can create range anxiety and discourage EV adoption, limiting the overall impact and accessibility of electric vehicles. Furthermore, the type of charging stations available, from fast-charging to slow-charging options, needs to cater to various needs and driving habits, ensuring a seamless and reliable charging experience for all.
Addressing the Charging Needs of Different Vehicle Types
Electric vehicles come in a variety of sizes, power levels, and intended use cases. This diversity necessitates a charging infrastructure that can accommodate various vehicle types. From compact city cars to large SUVs and trucks, the charging requirements differ considerably. Consequently, the infrastructure must provide options for different charging speeds and power outputs to satisfy the needs of each vehicle type.
Furthermore, the charging needs of commercial EVs, such as delivery vans and buses, warrant particular attention. These vehicles typically require more significant charging capacity and potentially faster charging solutions to maintain operational efficiency. A dedicated charging infrastructure for commercial vehicles will be essential for supporting this sector's transition to electric power.
The Impact of Charging on Last-Mile Delivery
The integration of electric vehicles into last-mile delivery systems is poised to revolutionize logistics. With the ability to charge quickly and efficiently at strategically placed locations, electric delivery vehicles can optimize routes and reduce emissions significantly. This, in turn, creates a more sustainable and environmentally friendly delivery model, impacting not just the delivery process, but also the overall urban landscape and the local air quality.
However, the widespread adoption of electric delivery vehicles also necessitates the development of charging stations specifically designed for high-volume, commercial use. The sheer number of vehicles needing to charge frequently necessitates robust infrastructure and reliable charging solutions to support the growing demand.
Incentivizing EV Adoption Through Charging Policies
Government policies and incentives can play a crucial role in encouraging EV adoption. Subsidies for home charging installations, favorable tax policies for purchasing EVs, and incentives for businesses to invest in charging infrastructure can stimulate the market and accelerate the shift towards electric vehicles. These policies should consider the varying needs of different socioeconomic groups, ensuring equitable access to electric mobility solutions.
Furthermore, clear regulations and standards for charging infrastructure will ensure interoperability and reliability. This will help to mitigate range anxiety and provide consumers with a consistent and dependable experience, ultimately boosting the widespread acceptance of electric vehicles.

Read more about How EVs Are Revolutionizing Last Mile Delivery
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies