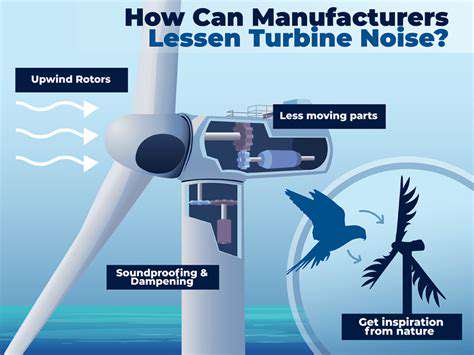
Noise Reduction in Wind Energy Advancements: Community Acceptance
The Growing Importance of Noise Reduction in Wind Energy
Understanding the Fundamentals of Noise
Noise, often perceived as a nuisance, plays a surprisingly crucial role in various fields, from environmental science to engineering. Understanding the characteristics of noise, including its amplitude, frequency, and duration, is essential for effective mitigation and management strategies. Noise pollution, in its many forms, can have detrimental impacts on human health and well-being. Identifying the sources of noise is the first step in developing targeted solutions.
Noise, in its physical manifestation, is often characterized by unwanted sounds. This unwanted quality is subjective and depends heavily on the context. What may be considered acceptable noise in one environment could be perceived as a significant disturbance in another.
Noise Pollution and its Effects
Noise pollution, a growing concern globally, is a significant contributor to environmental degradation. Its impact extends beyond mere annoyance, encompassing a range of negative effects on human health, including stress, hearing loss, and sleep disruption. Chronic exposure to high levels of noise can lead to long-term health problems.
Environmental noise pollution affects wildlife as well, disrupting communication patterns, breeding cycles, and overall behavioral patterns. The impact on ecosystems is multifaceted and requires careful consideration in mitigation strategies.
Noise Control Techniques in Various Industries
Industrial settings often generate significant noise levels, requiring robust noise control measures to protect worker health and comply with regulations. Implementing soundproofing measures, such as using noise barriers and sound absorption materials, is crucial for minimizing noise transmission.
Construction sites, another major source of noise, also necessitate effective noise control strategies to minimize disruption to surrounding communities. This often involves implementing temporary noise barriers and limiting operating hours.
Technological Advancements in Noise Reduction
Technological advancements have led to innovative solutions for noise reduction. New materials and designs are being developed to effectively absorb and block sound waves, creating quieter environments in a variety of settings. These advancements are essential for creating more peaceful and productive environments.
The development of active noise cancellation technologies is another significant advancement. These technologies utilize sound waves to counteract existing noise, effectively reducing its impact. These technologies are increasingly prevalent in consumer electronics, automotive engineering, and even in personal protective equipment.
Noise Monitoring and Measurement Techniques
Accurate noise monitoring and measurement are crucial for assessing noise levels and evaluating the effectiveness of noise control measures. Specialized equipment, such as sound level meters, is used to collect data on noise levels and characteristics, providing valuable insights for targeted interventions.
Different measurement techniques are employed depending on the specific application and the type of noise being measured. Understanding these techniques is crucial for accurate assessment and effective mitigation of noise pollution in various contexts.
The Future of Noise Management
The future of noise management hinges on a multi-faceted approach that combines technological innovation, policy interventions, and public awareness. Proactive measures aimed at noise reduction are critical for preserving public health and well-being.
Encouraging the use of quieter technologies, promoting sustainable practices, and implementing stricter noise regulations are all vital steps in the ongoing effort to manage and reduce noise pollution effectively. These efforts will contribute to healthier and more peaceful environments for everyone.

Read more about Noise Reduction in Wind Energy Advancements: Community Acceptance
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies