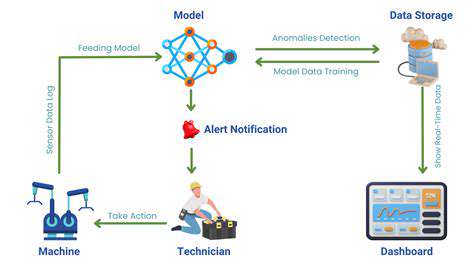
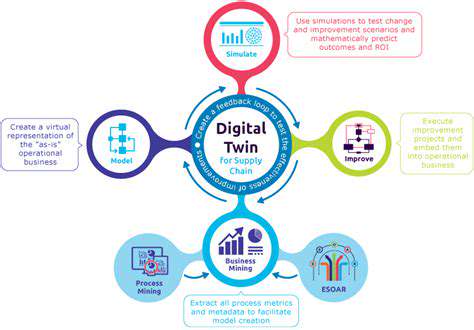
Offshore Wind for Island Nations

Economic Stimulation and Growth
The influx of investment capital spurred by innovative technologies often leads to significant economic stimulation. New businesses, fueled by these advancements, create a ripple effect, boosting demand for goods and services throughout the economy. This increased demand, in turn, drives employment growth and fosters a more robust and dynamic economic landscape. This is particularly important in regions facing economic stagnation, as the introduction of new technologies can revitalize local economies and create numerous opportunities for job creation and skill development.
Furthermore, the development and implementation of new technologies frequently necessitate the creation of specialized jobs in areas like research and development, engineering, and technical support. These roles, often requiring advanced skills and expertise, attract highly qualified individuals and contribute to a more skilled and productive workforce. This, in turn, can increase overall productivity and enhance the competitiveness of businesses and industries in the global marketplace. The economic benefits extend beyond the immediate impact on the technology sector itself, contributing to a wider economic growth trajectory.
Job Creation Across Sectors
The impact of technological advancements extends beyond the immediate sphere of the technology sector itself. Numerous jobs are created in related industries, supporting the development and implementation of the new technologies. This includes roles in manufacturing, logistics, and sales, as well as support services like marketing, customer service, and maintenance. These diverse job opportunities contribute to a more balanced and resilient economy.
Beyond these direct job creations, the increased efficiency and productivity enabled by new technologies often lead to cost reductions for businesses. This allows companies to invest further in their operations, potentially creating more jobs in the long run. This indirect impact on job creation is crucial to the sustained growth and development of the economy.
Skill Development and Workforce Enhancement
The introduction of new technologies often necessitates the development of new skills and expertise within the workforce. This creates a demand for training and education programs designed to equip individuals with the necessary knowledge and abilities to thrive in the evolving technological landscape. These programs, in turn, contribute to a more skilled and adaptable workforce, which is essential for businesses to remain competitive in the global market. This skill development is not just limited to the technology sector, but extends to many other sectors of the economy as well.
Investing in skill development and workforce enhancement programs is critical to ensuring that individuals can adapt to the changing demands of the job market. This creates a workforce that is better equipped to handle the complexities and challenges of a technology-driven economy. This, in turn, leads to higher productivity, greater economic stability, and improved quality of life for workers.
Environmental Considerations: Minimizing Impact and Maximizing Sustainability
Minimizing Environmental Impact of Mini-Products
The production and use of miniaturized products, while offering numerous advantages, raise important environmental concerns. Careful consideration must be given to the entire lifecycle of these products, from raw material extraction to disposal. Minimizing the environmental footprint of mini-products requires a holistic approach that considers all stages of their existence. This includes using sustainable materials, optimizing manufacturing processes, and designing for recyclability and reuse.
One key aspect is the selection of materials. Using recycled or renewable materials in the manufacturing process can significantly reduce the environmental impact of mini-products. This also includes reducing the amount of virgin materials used, thus minimizing the strain on natural resources and the associated environmental damage.
Material Selection and Sustainability
The materials used in the production of mini-products play a crucial role in their environmental impact. Choosing sustainable materials is essential for minimizing the environmental toll of these increasingly prevalent products. This includes considering the entire lifecycle of the material, from its extraction to its eventual disposal, to assess its environmental impact. A shift towards bio-based materials and recycled content is crucial for creating a more sustainable miniaturization industry.
Using recycled materials reduces the demand for new raw materials, preserving natural resources and minimizing waste. The choice of materials has a significant impact on the overall environmental performance of mini-products, therefore, careful consideration must be given to their origin and impact on the environment.
Manufacturing Processes and Energy Efficiency
Miniaturization often necessitates advanced manufacturing techniques. These techniques, while enabling the creation of smaller and more complex products, can also have significant energy implications. Minimizing energy consumption during the manufacturing process is crucial to reduce the carbon footprint of mini-products. Optimizing production lines and utilizing energy-efficient technologies are essential steps in this direction.
Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize waste and reduce the overall energy consumption needed to produce mini-products. Adopting sustainable manufacturing practices, such as lean manufacturing principles and circular economy models, can help reduce the environmental impact of the miniaturization industry.
Waste Management and Product Lifespan
The disposal of mini-products poses a unique challenge. These products, often containing intricate components, can be difficult to recycle or reuse. Designing mini-products with recyclability in mind is essential. This includes the use of standardized components and modular designs, facilitating the separation and reuse of materials.
Designing for a longer lifespan and ease of repair is also crucial. This reduces the need for frequent replacements and the generation of e-waste. Promoting the reuse and refurbishment of mini-products is another important aspect of minimizing their environmental impact. This also includes promoting take-back programs and proper disposal mechanisms to ensure responsible end-of-life management.
Read more about Offshore Wind for Island Nations
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies