Sustainable Supply Chains: Measuring and Reducing Environmental Footprint with Tech
Understanding Environmental Footprint Quantification
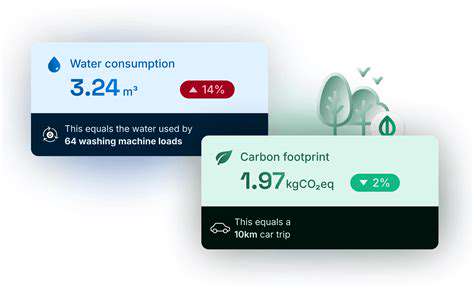
Quantifying environmental footprint is a crucial aspect of understanding and addressing the impact of human activities on the planet. It involves measuring the use of natural resources and the generation of waste across various stages of a product's lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. This measurement allows us to identify areas of high environmental impact and develop strategies to minimize them. This process is essential for informed decision-making regarding environmental sustainability.
Methods for Calculating Environmental Impact
Numerous methods exist for calculating environmental footprints, each with its own strengths and limitations. These methods often rely on standardized datasets and methodologies, allowing for comparisons across different products, industries, and regions. A common method is life cycle assessment (LCA), which evaluates the environmental impacts throughout a product's entire life cycle, from cradle to grave. Other approaches may focus on specific environmental indicators like carbon emissions, water consumption, or waste generation.
The Importance of Data Collection and Analysis
Accurate quantification of environmental footprints relies heavily on comprehensive data collection and rigorous analysis. This involves gathering detailed information on resource use, emissions, and waste generation at each stage of a product's lifecycle. Data accuracy is paramount for reliable results and informed decision-making. Data analysis tools and software play a critical role in processing and interpreting the collected data to identify key trends and patterns.
Applications of Footprint Quantification
The results of environmental footprint quantification are applicable across a wide range of sectors. Businesses can use these insights to identify areas for improvement in their operations and supply chains. Consumers can use this information to make more sustainable purchasing decisions. Governments can use these data for policy development and environmental regulation.
Challenges in Footprint Quantification
Despite its importance, quantifying environmental footprints faces several challenges. Data availability and accuracy can be problematic, particularly for complex products and systems. Standardization and comparability across different methodologies and datasets can also be difficult. Furthermore, the dynamic nature of environmental systems and the constantly evolving understanding of these systems adds another layer of complexity.
Future Directions and Technological Advancements
Future advancements in environmental footprint quantification hinge on technological innovations and the development of more sophisticated methodologies. Improved data collection techniques and more accessible data platforms are crucial to enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of the process. Integrating environmental footprint assessments into decision-making processes at various levels, from individual consumers to global corporations, is another significant area of development. Integrating these considerations into product design and manufacturing processes will be essential for creating a more sustainable future.
The Future of Sustainable Supply Chains: A Collective Effort
Innovation in Sourcing
Sustainable supply chains demand innovative sourcing strategies, moving beyond traditional methods to prioritize ethical and environmentally conscious practices. This involves actively seeking out suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their environmental footprint, fair labor practices, and responsible resource management. Companies need to establish robust due diligence processes to verify the sustainability claims of their suppliers, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the entire supply chain. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters trust and strengthens relationships with partners who share a similar vision for a sustainable future.
Technology Integration
Technology plays a crucial role in driving efficiency and transparency within sustainable supply chains. Implementing blockchain technology, for instance, can enhance traceability, ensuring that products are sourced ethically and manufactured sustainably. Digital platforms can facilitate communication and collaboration among stakeholders, enabling real-time monitoring of supply chain activities. Data analytics can provide insights into environmental impact and social responsibility, allowing companies to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions. Ultimately, technology integration is not just a trend but a necessity for modern sustainable supply chains.
Circular Economy Principles
Embracing circular economy principles is vital for minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization. This involves designing products for durability and recyclability, promoting reuse and repair, and implementing closed-loop systems for material recovery. By shifting from a linear take-make-dispose model to a circular one, companies can significantly reduce their environmental impact and create a more sustainable future. This approach fosters innovation in product design, encourages partnerships, and creates new economic opportunities.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Sustainable supply chains are not built in isolation; they require collaborative efforts among various stakeholders. Companies need to partner with NGOs, governments, and other businesses to share knowledge, resources, and best practices. Collaborations can foster innovation, drive policy changes, and create shared responsibility for environmental protection and social justice. Open communication and shared goals are essential for building effective and resilient supply chains that prioritize sustainability. This collaborative spirit is key to achieving meaningful change.
Consumer Engagement
Consumers play a critical role in driving demand for sustainable products and practices. Transparency in supply chain information empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions. Educational initiatives and campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of sustainable choices. By engaging consumers in the sustainability journey, companies can build a powerful collective force for change. This engagement fosters a culture of responsibility and motivates businesses to prioritize ethical and environmentally conscious practices.
Measuring and Reporting Progress
Measuring and reporting progress on sustainability goals is essential for accountability and continuous improvement. Companies need to establish robust metrics to track their environmental and social performance. Transparency in reporting allows stakeholders to assess the effectiveness of sustainability initiatives and hold companies accountable for their commitments. Regular audits and certifications can validate progress and build trust. Ultimately, consistent measurement and reporting are crucial for demonstrating a genuine commitment to sustainable practices and inspiring other companies to follow suit. This transparency fosters trust and encourages accountability.
Read more about Sustainable Supply Chains: Measuring and Reducing Environmental Footprint with Tech
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies