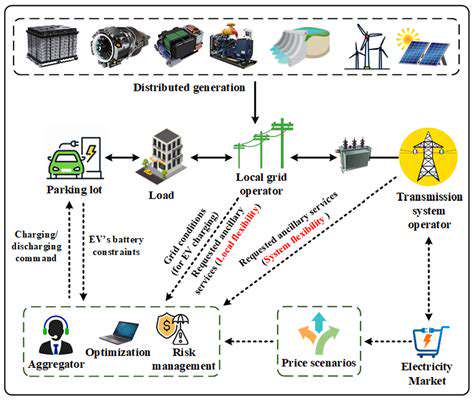
How Fleet Electrification Reduces Operational Costs
Lowering Repair Costs
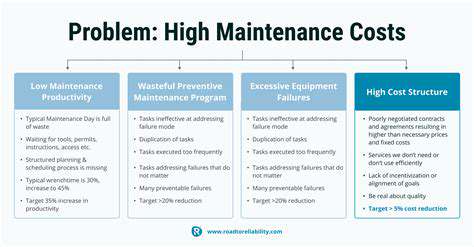
Implementing preventative maintenance strategies offers significant financial benefits by reducing repair costs. Addressing potential issues before they escalate minimizes breakdown frequency and severity. This approach directly lowers repair expenses and decreases equipment downtime. Routine inspections and timely part replacements prevent costly overhauls and unexpected shutdowns.
Predictive maintenance, utilizing sensor data and analytics, anticipates failures before they occur. Identifying performance patterns allows for scheduled repairs, reducing operational disruptions. Proactive maintenance proves more cost-effective than reactive repairs in the long run.
Proactive Maintenance Scheduling
Strategic maintenance scheduling ensures critical components receive attention at optimal times. This prevents unexpected breakdowns that could disrupt production or service delivery. Advance planning enables efficient resource allocation and minimizes operational impact.
Improved Equipment Lifespan
Regular maintenance extends equipment life by preventing premature wear. Proper lubrication, cleaning, and component replacements contribute to asset longevity. Preventative maintenance represents an investment in equipment's future performance. Fewer replacements translate to substantial long-term savings.
Minimized Downtime
Robust maintenance plans significantly reduce unexpected downtime. Equipment failures can cause substantial productivity and revenue losses. Predictive analytics in maintenance schedules help prevent breakdowns and maintain smooth operations. Consistent workflow maintenance prevents unnecessary delays.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Well-maintained equipment ensures smooth production and service delivery. Reliable machinery prevents interruptions that could affect output. Efficient systems increase profitability while reducing error-related costs. Preventative maintenance remains crucial for operational excellence.
Reduced Risk of Accidents
Regular maintenance identifies and addresses safety hazards before accidents occur. This proactive safety approach protects employees while minimizing legal and regulatory risks. Safe work environments naturally enhance productivity.
Reduced Inventory Costs
Preventative maintenance decreases emergency repair needs, reducing spare parts inventory. Efficient maintenance lowers inventory expenses and prevents production schedule disruptions. Predictive maintenance enables better spare parts management.
Minimized Emissions and Associated Costs: Beyond the Bottom Line
Minimizing Emissions: A Shift in Corporate Responsibility
The transition to electric fleets represents more than emission reduction—it signifies evolving corporate responsibility. Businesses increasingly recognize environmental sustainability as integral to strategy, driven by public awareness, regulations, and long-term savings potential. Maintaining positive public image and attracting eco-conscious stakeholders has become essential.
Beyond environmental benefits, companies gain improved brand reputation and employee engagement. Workers prefer employers with strong ethical values and sustainability commitments. Demonstrating environmental responsibility fosters workforce motivation.
While electric vehicle transition requires substantial initial investment in vehicles, charging infrastructure, and training, companies recognize long-term value through reduced maintenance, fewer fuel-related disruptions, and potential government incentives. Comprehensive lifecycle cost analysis proves crucial for successful electrification.
Quantifying the Costs: Beyond the Initial Investment
Electric fleet conversion demands thorough total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis, considering purchase price, charging infrastructure, maintenance differences, incentives, and long-term fuel savings. This holistic TCO approach enables informed electrification decisions. Lifecycle cost consideration remains essential for successful implementation.
Indirect costs including supply chain adjustments, driver retraining, and maintenance procedure adaptations require careful evaluation. Understanding these complexities helps mitigate transition risks. Strategic electrification planning must address potential supply chain disruptions.
Low-carbohydrate diets have gained popularity in contemporary nutrition, often praised for potential weight management and wellness benefits. These approaches emphasize reducing carbohydrate intake, the body's primary energy source. Understanding reduced-carb eating's metabolic effects proves essential for personal suitability assessment.
Increased Vehicle Lifespan and Reduced Repair Costs: Strategic Planning for Savings
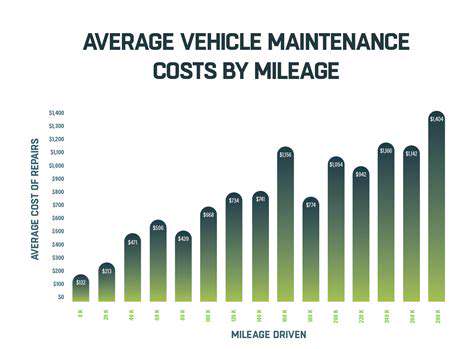
Extended Vehicle Lifespan
Modern manufacturing and maintenance advancements have significantly extended vehicle lifespans. Improved materials, engineering designs, and production processes create more durable, wear-resistant vehicles. Fewer mechanical failures and longer intervals between major repairs allow extended ownership periods.
Accessible, affordable maintenance services and readily available parts facilitate vehicle upkeep. This proactive maintenance approach, combined with modern vehicle resilience, substantially contributes to longevity.
Reduced Repair Costs
Extended vehicle lifespans typically lower long-term repair costs. While initial maintenance requires investment, reduced repair frequency decreases overall ownership expenses. This benefit allows consumers to budget more effectively for vehicle maintenance.
Preventive maintenance minimizes need for costly repairs. Addressing minor issues promptly through scheduled maintenance often prevents major repairs.
Enhanced Vehicle Reliability
Modern vehicles prioritize reliability through advanced engineering and quality control. Components demonstrate greater durability compared to older models, resulting in fewer unexpected failures. This reliability ensures more consistent driving experiences.
Advanced diagnostic and repair technologies further enhance reliability by enabling rapid, accurate issue identification and resolution.
Improved Fuel Efficiency
Many contemporary vehicles achieve superior fuel efficiency through advanced engine technology and aerodynamic designs. Reduced fuel consumption lowers operating costs and environmental impact. These efficiency gains benefit both drivers and the environment.
Safety Features and Driver Assistance
Modern vehicles incorporate advanced safety systems and driver-assistance technologies. Features like airbags, ABS, and ESC significantly reduce accident severity and potential fatalities. Additional systems including adaptive cruise control and lane departure warnings enhance safety and driving comfort.
Incentives and Government Support: Leveraging Opportunities for Savings

Financial Incentives
Government financial incentives stimulate innovation and growth in targeted sectors through tax breaks, grants, and subsidies. These incentives encourage investment in areas deemed crucial for national development. Renewable energy tax credits, for example, reduce financial burdens, making sector investment more attractive.
Effective incentive design requires careful consideration to ensure market fairness and avoid unintended consequences. Well-structured programs can drive significant economic activity and technological progress.
Research and Development Funding
Dedicated R&D funding drives innovation across universities, research institutions, and private companies. Government support proves particularly valuable for early-stage projects where private investment remains limited.
Infrastructure Development
Modern infrastructure underpins economic development. Government investment in transportation, communication, and energy systems creates supportive business environments. Enhanced infrastructure boosts connectivity, efficiency, and economic growth while creating employment opportunities.
Regulatory Frameworks
Supportive regulatory environments attract investment and encourage innovation. Clear, predictable regulations promote stability, enabling business expansion and market competitiveness.
Education and Skill Development
Skilled workforces drive economic growth. Government-supported education and training programs ensure workers meet evolving economic demands. Human capital investment yields long-term returns through increased productivity and innovation.
Public-Private Partnerships
Collaborative PPPs combine government resources with private sector efficiency for impactful projects. These partnerships often achieve more ambitious outcomes than either sector could accomplish independently. The approach frequently results in innovative, cost-effective solutions.
International Cooperation
Global collaboration accelerates progress through knowledge and technology sharing. International partnerships provide access to global markets and expertise, fostering innovation across sectors including healthcare, technology, and sustainability.
Read more about How Fleet Electrification Reduces Operational Costs
Hot Recommendations
- How Your Rooftop Solar Contributes to the Grid
- Solar Energy for Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
- Offshore Wind Repowering
- Agricultural Solar (Agrivoltaics): Synergies Between Food and Energy
- Airborne Wind Energy: Tapping High Altitude Winds
- Renewable Energy and Green Hydrogen: A Powerful Duo
- Geothermal Power Plant Technologies: Flash, Dry Steam, and Binary Cycle
- The Future of Offshore Wind Transmission
- The Role of Energy Storage in Enhancing Energy Security
- The Environmental Footprint of Modern Wind Energy Advancements: LCA Analysis