Investing in the Renewable Energy Revolution: Opportunities Await

Beyond the Solar and Wind Paradigm: A Broader Energy Landscape
The world is increasingly recognizing the limitations of solely relying on solar and wind power for a sustainable energy future. While these renewable sources are crucial, they are not a panacea. Their intermittent nature necessitates the development of complementary technologies and energy storage solutions to ensure a reliable and stable energy grid. This exploration delves into a wider spectrum of energy options, exploring the potential of innovative approaches to meet the growing global energy demand sustainably.
Harnessing the Power of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy, tapping into the Earth's internal heat, offers a compelling alternative. This renewable resource is consistently available, regardless of weather conditions, making it a valuable component of a diversified energy portfolio. Deep geothermal reservoirs provide a stable and reliable energy source, but the infrastructure required for extraction and transmission needs careful consideration.
Geothermal power plants, while often located in specific geographic areas, can significantly contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels in those regions. The environmental impact of geothermal operations, however, should be meticulously assessed and mitigated.
Exploring the Potential of Tidal and Wave Energy
The rhythmic power of tides and waves represents a largely untapped potential. Harnessing these natural forces through innovative technologies can provide a consistent energy source, particularly in coastal regions. Ocean currents and wave energy offer a promising pathway to a cleaner energy future, but the technology for efficient capture and conversion needs further development and refinement.
Nuclear Fusion: A Long-Term Energy Solution?
Nuclear fusion, the process that powers the sun, holds the promise of a virtually limitless energy source. Despite significant research and development efforts, achieving controlled nuclear fusion reactions remains a significant scientific challenge. Overcoming these hurdles could pave the way for a clean and abundant energy source for generations to come, but the timeline for widespread implementation is uncertain.
Advanced Bioenergy and Biofuels: Sustainable Alternatives
Exploring the potential of bioenergy and biofuels requires careful consideration of environmental impacts. Sustainable agricultural practices and careful waste management are essential to avoid negative consequences for food security and biodiversity. Bioenergy offers a potentially viable alternative to fossil fuels, but the carbon footprint of various feedstocks and conversion processes must be rigorously assessed.
Energy Storage: Bridging the Intermittency Gap
Energy storage technologies are critical to overcoming the intermittency challenges of renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Advanced battery technologies, pumped hydro storage, and other innovative solutions are essential to ensure a reliable and stable energy grid. Developing cost-effective and scalable energy storage solutions is critical to integrating intermittent renewables into the energy mix and creating a more sustainable energy future.
The Financial Incentives and Policy Support

Government-backed Initiatives
Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the critical role of financial incentives in stimulating economic growth and promoting desired societal outcomes. These initiatives often take the form of tax breaks, subsidies, or grants aimed at specific industries or sectors. For example, tax credits for renewable energy investments can encourage businesses to adopt cleaner technologies, ultimately reducing carbon emissions. Such incentives can also support innovation and job creation.
Government-backed initiatives are designed to correct market failures and create a more favorable environment for specific sectors. These measures can be highly effective in driving market demand and fostering economic activity in areas deemed strategically important.
Tax Policies and Deductions
Tax policies play a crucial role in shaping financial incentives. Tax deductions, exemptions, and credits can directly reduce the financial burden on businesses and individuals, boosting their ability to invest and consume. For instance, deductions for charitable contributions encourage philanthropy and support social welfare programs. These policies often reflect societal priorities and values.
By influencing the effective tax rate, these policies can have a significant impact on investment decisions. Understanding how these policies are structured and their potential impact is vital for informed economic decision-making.
Subsidies and Grants
Subsidies and grants are another form of financial incentive offered by governments to promote specific activities or industries. These direct financial assistance programs are often targeted at sectors perceived as essential for national development. Renewable energy projects, for example, may receive substantial subsidies to encourage their adoption and foster a transition away from fossil fuels.
These forms of support are often designed to bridge financial gaps for businesses or individuals engaging in activities aligned with national priorities. Careful consideration of the appropriate use of subsidies is essential to prevent distortions in the market and ensure efficient allocation of resources.
Investment Incentives
Investment incentives are designed to encourage capital investment in specific projects or industries. These incentives can include tax breaks, expedited depreciation allowances, or specific grants for infrastructure projects. This type of incentive is often used to stimulate job creation and economic activity in lagging regions or sectors.
Companies are more likely to invest in regions or projects with attractive incentives, leading to increased employment opportunities and economic growth. Investment incentives can be a powerful tool for fostering economic growth in targeted areas.
Financial Incentives for Research and Development
Research and development (R&D) is crucial for technological advancement and economic progress. Financial incentives, such as tax credits and grants, can play a vital role in encouraging innovation and supporting the development of new products and technologies. These incentives help fund the often lengthy and expensive processes of R&D, ensuring that valuable research initiatives are pursued.
By stimulating innovation, these incentives can lead to breakthroughs in various fields, from medicine and technology to agriculture and energy. Ultimately, such financial support can have a profound impact on society's future.
Targeted Incentives for Specific Industries
Many nations utilize targeted financial incentives to foster the growth of specific industries deemed critical to their economic future. These incentives may include tax breaks, subsidies, or grants for industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, or renewable energy. This strategic approach aims to strengthen the nation's competitive position in the global market.
Such concentrated support can help industries overcome challenges and achieve economies of scale, leading to increased productivity and competitiveness. The selection of industries for targeted support requires careful consideration of national priorities and long-term economic goals.
International Financial Incentives and Trade Agreements
International trade agreements and financial incentives often play a significant role in shaping global economic activity. Countries may offer incentives to attract foreign investment or promote exports. These measures can influence the flow of capital and goods across borders, affecting global trade patterns. Understanding these global dynamics is essential for navigating the complex landscape of international commerce.
International financial incentives are often intertwined with trade agreements, creating a complex web of regulations and opportunities for businesses operating on a global scale. The interplay between these factors can significantly impact the competitiveness of nations and businesses in the global economy.
The evolving legal landscape necessitates a constant reassessment of established precedents and interpretations. The interplay between technological advancements and societal norms often forces courts to confront novel legal challenges, demanding a nuanced understanding of existing frameworks. This necessitates a proactive approach to legal research and analysis, ensuring that interpretations remain relevant and applicable in the face of dynamic change.
Mitigating Risks and Maximizing Returns
Understanding the Risks
Investing in renewable energy presents a unique set of risks, distinct from traditional investments. Fluctuating government policies, particularly regarding subsidies and regulations, can significantly impact project profitability. The inherent variability of weather patterns can also affect the output of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, leading to inconsistent revenue streams. Furthermore, technological advancements can lead to faster obsolescence of current equipment, making existing investments less valuable over time.
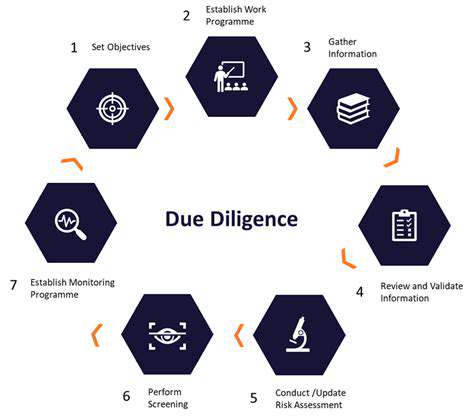
The development of new technologies, while promising, can also introduce unforeseen challenges. For example, the reliability and scalability of emerging storage solutions, crucial for grid integration, remain uncertain. Market competition, with new entrants and established players vying for market share, can also affect profitability margins. Therefore, thorough due diligence and a comprehensive understanding of the specific risks associated with each investment opportunity are paramount.
Evaluating Potential Returns
While risks are inherent, the potential returns in the renewable energy sector are substantial. Investment in this sector can yield strong returns by capitalizing on the growing global demand for clean energy. As governments worldwide implement policies to combat climate change, the market for renewable energy technologies is poised for significant expansion. This presents lucrative opportunities for investors who can identify and capitalize on emerging trends.
The long-term stability of renewable energy investments is often overlooked but is a key factor. As the world transitions to cleaner energy sources, the demand for these technologies is likely to remain high. Consequently, investments in established and emerging renewable energy companies can provide a stable and potentially high-yielding return over the long term. Careful analysis of market trends and company performance is essential to assess these potential returns accurately.
Diversification Strategies
Diversification is crucial in mitigating risks within the renewable energy sector. Investors should consider diversifying their portfolio across different renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal. This diversification reduces reliance on any single technology's performance and potentially shields against unforeseen challenges specific to one type of renewable energy source.
Geographic diversification is also important. Investments in renewable energy projects across various regions offer a broader perspective on market trends and regulatory environments, reducing the impact of localized risks. This approach can provide greater resilience to economic downturns or policy shifts in specific geographical areas.
Analyzing Market Trends
Thorough analysis of market trends is essential for successful investments in renewable energy. Tracking government policies, technological advancements, and consumer demand for clean energy solutions provides valuable insights into the sector's future trajectory. Staying updated on the latest innovations in energy storage, grid integration, and efficiency improvements is crucial for informed investment decisions.
Understanding the evolving landscape of regulatory frameworks, incentives, and environmental policies across different regions is critical. These factors significantly influence the viability and profitability of renewable energy projects, and changes in these regulations can dramatically impact investment returns. Therefore, ongoing market research and analysis are vital for maximizing returns and mitigating risks in this dynamic sector.
Financial Modeling and Due Diligence
Accurate financial modeling is paramount for evaluating the potential profitability and risks of renewable energy investments. Models should incorporate factors like project costs, revenue projections, and potential regulatory changes. Thorough due diligence is essential, including a deep dive into the financial health and operational capabilities of the companies or projects under consideration.
Careful consideration of long-term operational costs, maintenance requirements, and potential disruptions should also be incorporated into the financial models. This proactive approach helps investors anticipate and prepare for potential challenges, ensuring that their investments are aligned with realistic expectations of return and risk. A thorough understanding of the financial and operational aspects of an investment is critical for maximizing returns and minimizing losses.
Read more about Investing in the Renewable Energy Revolution: Opportunities Await
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies