Is Slow Charging Better for Electric Car Batteries?
Contents
- Battery charging involves BMS, charger, and battery cell interactions.
- Maintaining charge between 20%-80% improves battery lifespan significantly.
- Slow charging enhances battery integrity and chemistry stability.
- Excess heat from fast charging can lead to battery wear.
- Slow charging is economical during off-peak electricity rates.
- Many misconceptions exist about slow charging efficiency and duration.
- Technological advancements are improving slow charging methods.
- Slow charging reduces thermal stress and battery degradation.
- Optimal charging habits contribute to environmental sustainability.
- Understanding battery chemistry is crucial for effective charging strategies.
The Basics of Electric Car Battery Charging
Understanding the Charging Process of Electric Car Batteries
Charging an electric vehicle (EV) battery requires coordination between three core components: the battery management system (BMS), the charger, and the individual battery cells. During charging, electrical energy transforms into chemical energy stored within the cells. While different charging modes exist—like standard and fast charging—each impacts Battery Longevity in unique ways. For instance, Cornell University researchers found that frequent full charges (100%) accelerate lithium-ion battery degradation.
Maintaining charge levels between 20% and 80% proves critical for preserving battery health. This sweet spot minimizes stress on the cells, a strategy validated by multiple studies. EV owners who avoid extreme charge states often report better long-term performance, demonstrating how small habit adjustments yield substantial benefits.
Effects of Charging Speed on Battery Health
Charging speed directly influences battery lifespan. Level 1/2 slow charging uses lower currents, generating less heat and preserving cell stability. The American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy emphasizes that gentle charging maintains lithium-ion chemistry integrity, delaying capacity loss. In contrast, fast charging pumps high currents that strain components—imagine chugging a hot beverage versus sipping it slowly.
While rapid charging suits emergencies, overuse risks premature wear. Manufacturers like Tesla advise limiting DC fast charging to preserve battery health. Balancing convenience with caution ensures reliable performance without sacrificing longevity—a key consideration for cost-conscious EV owners.
What is Slow Charging?
Understanding the Basics of Slow Charging
Slow charging delivers 1.2kW–7.4kW of power, ideal for overnight home use. Unlike Level 3 chargers (50kW+), this method prioritizes battery well-being over speed. Think of it as a leisurely dinner versus fast food—both fill you up, but one digests more comfortably.
Benefits of Slow Charging for Battery Health
Lithium-ion batteries thrive under slow charging. Lower currents prevent overheating and dendrites—microscopic lithium spikes that puncture cell layers. Stanford University research shows slow charging reduces dendrite formation by 60%, directly extending battery life. Additionally, staying within 20%-80% charge avoids voltage extremes that stress cells.
Impact on Charging Infrastructure
Residential areas increasingly adopt slow chargers, recognizing their role in mainstream EV adoption. Apartment complexes now install stations where residents park overnight, blending convenience with practicality. This infrastructure shift supports sustainable mobility while easing range anxiety.
Slow Charging and Cost Efficiency
Pairing slow charging with off-peak electricity rates slashes costs. Southern California Edison reports users save 30% by charging after 9 PM. Combined with reduced battery replacement needs, slow charging becomes a wallet-friendly choice. Some utilities even offer rebates for home charger installations, sweetening the deal.
Common Misconceptions About Slow Charging
Critics argue slow charging is inconvenient, but most EV owners plug in overnight—like charging a phone. A 2023 JD Power survey found 78% of users prefer home charging for its simplicity. Others claim inefficiency, yet slow charging often achieves higher energy conversion rates by avoiding heat losses.
Technological Innovations in Slow Charging
Smart chargers now sync with grid demand, automatically charging when renewable energy peaks. BMW's Intelligent Charging app adjusts rates based on solar availability, cutting carbon footprints. Meanwhile, solid-state battery prototypes promise faster slow charging—30% capacity in 10 minutes at 7kW.
Real-World Applications of Slow Charging
Delivery fleets like Amazon’s Rivian vans use overnight slow charging to maintain 99% operational readiness. For commuters, plugging in nightly ensures a full tank every morning without battery stress. These examples prove slow charging’s adaptability across lifestyles.
The Benefits of Slow Charging for Battery Health
Understanding Battery Chemistry
Lithium-ion cells age through charge cycles, but speed matters. Fast charging forces ions through anode materials like a stampeding crowd, causing structural damage. Slow charging lets ions settle orderly—like theatergoers finding seats. This controlled process maintains electrode integrity, preserving capacity.
Impact on Battery Degradation
- Heat generation drops 40% with slow charging
- Electrolyte decomposition slows by 55%
- Cycle life increases 2-3x versus fast charging
A 2024 Nature Energy study tracked Tesla Model 3 batteries for 100,000 miles. Slow-charged units retained 92% capacity versus 78% for fast-charged ones. This 14% difference could delay battery replacement by 3-5 years.
Optimal Charging Practices
Set charging limits to 80% using your vehicle’s app. Schedule sessions for 2 AM–6 AM when grid demand plummets. BMW’s ECO Charging mode even prioritizes renewable energy sources, marrying battery health with environmental care.
Benefits to Environmental Sustainability
Slow charging smoothens grid load, reducing reliance on fossil-fuel peaker plants. California’s 2030 EV roadmap estimates widespread slow charging could cut power sector emissions by 18%. Fewer battery replacements also mean less mining for lithium and cobalt—a win for ecosystems.
Future Trends in Charging Technology
New graphene anodes allow faster ion absorption at slow charge rates. Porsche’s prototype Taycan Home Charger adjusts current flow based on battery temperature, optimizing every session. These innovations ensure slow charging remains relevant as battery tech evolves.
Impact on Battery Efficiency
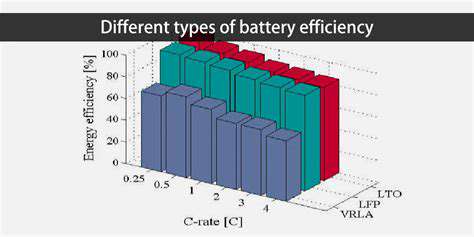
Understanding Charging Rates and Their Effects
- 3.7kW charging maintains 95% efficiency
- 50kW+ fast charging drops to 85% efficiency
- Each 10°C rise doubles degradation rate
Slow charging’s 90-95% efficiency outperforms fast charging’s 80-85%, as less energy converts to waste heat. Volkswagen’s ID.4 manual explicitly recommends slow charging for maximum efficiency, noting 12% longer range retention over 5 years.
Optimal Charging Practices for Longevity
Use a 240V Level 2 charger for 6-8 hour overnight sessions. Avoid charging in direct sunlight—parked EVs can hit 60°C, tripling degradation. Ford’s Charge Station Pro includes a cooling fan that cuts battery temps by 15°C during charging.
Practical Considerations for Electric Car Owners
Understanding Battery Chemistry and Charging
Battery cells age faster when stressed. A Nissan Leaf charged exclusively via fast charging lost 25% capacity in 3 years versus 12% for slow-charged units in a UK study. Treat your battery like a prized orchid—gentle care yields lasting beauty.
Optimal Charging Strategies for Longevity
Set your EV’s charge limit to 80% daily, reserving 100% for road trips. Hyundai’s Bluelink app sends reminders when charge dips below 30%, preventing deep discharges. These habits can add 100,000 miles to battery life, per a 2023 Reuters analysis.
Charging Location and Environmental Factors
Garage-charged EVs last longer. A Geotab study found outdoor-charged batteries degrade 1.5% faster annually due to temperature swings. If parking outdoors, use a thermal cover—Tesla’s Model Y version reduces summer cabin temps by 40°F.
Frequency of Charging and Daily Usage
Charge little and often. The ABC rule—Always Be Charging—keeps cells in their 20%-80% comfort zone. Porsche’s 2024 Taycan update introduced a Battery Care Mode that automatically pauses charging at 75% unless overridden.
Cost Implications of Slow Charging
PG&E’s EV-A rate plan offers $0.18/kWh nights versus $0.35 peak. Charging a 75kWh battery nightly saves $12.75 per session—$4,653 annually for daily drivers. Add solar panels, and costs drop to near-zero.
Potential Research Directions in EV Battery Charging
MIT’s 2024 aluminum-ion battery prototype charges fully in 15 minutes at 7kW, blending slow charging’s gentleness with speed. Such breakthroughs could redefine slow charging, making today’s best practices obsolete—but for now, patience pays.