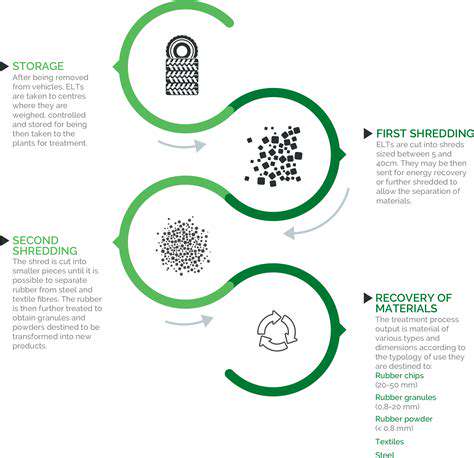
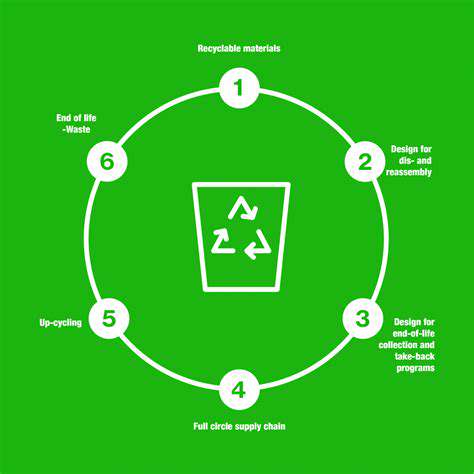
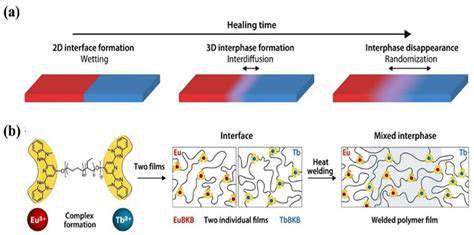
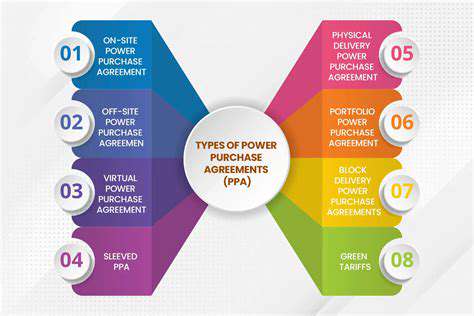
Energy Storage for Residential Homes

Integration with Renewable Energy Sources

Harnessing Solar Power
Integrating solar energy into existing power grids requires careful planning and execution. Solar panel installations need to be strategically placed to maximize sunlight exposure throughout the day, taking into account factors such as shading and weather patterns. Furthermore, efficient energy storage solutions, such as batteries, are crucial to address the intermittent nature of solar power generation, ensuring a consistent power supply even when the sun isn't shining.
The advancements in solar panel technology and their decreasing costs have made solar power a viable and increasingly popular option for residential and commercial use. This integration, when done properly, leads to significant reductions in reliance on fossil fuels and a substantial decrease in carbon emissions.
Wind Energy Integration
Wind energy, another crucial renewable resource, presents unique challenges for grid integration. The unpredictable nature of wind necessitates sophisticated forecasting tools and control systems to manage fluctuating power output effectively. These systems need to be able to anticipate and respond quickly to changes in wind speed to maintain grid stability.
Hydropower's Role
Hydropower, a reliable source of renewable energy, can be integrated into existing infrastructure by upgrading existing dams and reservoirs to maximize energy output. Careful consideration of environmental impacts and potential disruptions to local ecosystems is essential during the planning and implementation stages of these projects.
The integration of hydropower with other renewable sources can create a more resilient and stable energy system, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Geothermal Energy Potential
Geothermal energy, derived from the Earth's internal heat, offers a consistent and reliable power source, independent of weather conditions. However, the geographic limitations of suitable geothermal resources must be carefully evaluated and geographically identified for optimal utilization. Exploration and development of geothermal resources require significant upfront investment and specialized expertise.
Energy Storage Solutions
A critical component of integrating renewable energy sources is effective energy storage. Reliable and scalable battery storage systems are essential to address the intermittency of solar and wind power, ensuring a constant and stable power supply. Research and development in this area are crucial for further advancements in grid integration.
Different types of storage technologies, such as pumped hydro storage and thermal energy storage, offer diverse approaches to addressing this challenge. Each technology has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, requiring careful consideration of local conditions and project goals.
Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grids, equipped with advanced sensors and communication technologies, are crucial for managing the fluctuating nature of renewable energy sources. These grids enable real-time monitoring and control of energy flow, optimizing the integration of different renewable energy sources. Smart grids also facilitate the integration of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar panels, into the broader energy system.
The implementation of smart grid technologies not only enhances the efficiency and reliability of the entire energy system but also empowers consumers to participate actively in managing their energy usage and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Successful integration of renewable energy requires supportive policy and regulatory frameworks. Government incentives and policies can significantly drive investment and development in renewable energy technologies and infrastructure. Clear regulations regarding grid access and interconnection are essential to facilitate the smooth flow of renewable energy into the existing power grid. These policies must be designed to balance environmental protection with economic growth and energy security.

Read more about Energy Storage for Residential Homes
Hot Recommendations
- Offshore Wind for Industrial Power
- Agrivoltaics: Dual Land Use with Solar Energy Advancements: Sustainable Farming
- Hydrogen as an Energy Storage Medium: Production, Conversion, and Usage
- Utility Scale Battery Storage: Successful Project Case Studies
- The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Peak Shaving
- The Role of Startups in Renewable Energy
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization of Energy Generation
- The Future of Wind Energy Advancements in Design
- Synchronous Condensers and Grid Inertia in a Renewable Energy Grid
- Corporate Renewable Procurement for Government Agencies